Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Solution
Given,
Diameter of the sun = 1.4 × 109 m
Distance between sun and earth is taken as object distance (u) = − 150 × 1011 cm,
Focal length (f) of the lens = 20 cm
Using lens formula,
\[\frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
The object distance is very large as compared to focal length of the lens.
Hence, the image is formed at the focus.
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{20} - \frac{1}{150 \times {10}^{11}}\]
\[= \frac{750 \times {10}^9 - 1}{150 \times {10}^{11}}\]
\[\simeq \frac{750 \times {10}^9}{150 \times {10}^{11}}\]
\[\Rightarrow v = \frac{150 \times {10}^{11}}{750 \times {10}^9}\]
We know, Magnification (m) is given by:
\[(m) = \frac{v}{u} = \frac{h_2}{h_1}\]
\[\Rightarrow h_2 = \frac{v}{u} \times h_1\]
\[= \frac{150 \times {10}^{11}}{750 \times {10}^9 \times 150 \times {10}^{11}} \times 0 . 7 \times {10}^{12} mm\]
\[ = 0 . 93 mm\]
Hence, the required radius of the image of the sun is 0.93 mm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
Suppose you are inside the water in a swimming pool near an edge. A friends is standing on the edge. Do you find your friend taller or shorter than his usual height?
The image formed by a concave mirror
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.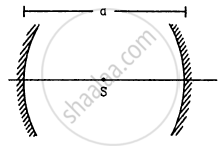
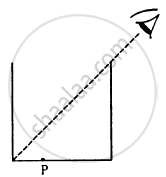
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

A cylindrical vessel, whose diameter and height both are equal to 30 cm, is placed on a horizontal surface and a small particle P is placed in it at a distance of 5.0 cm from the centre. An eye is placed at a position such that the edge of the bottom is just visible (see figure). The particle P is in the plane of drawing. Up to what minimum height should water be poured in the vessel to make the particle P visible?
An optical fibre (μ = 1.72) is surrounded by a glass coating (μ = 1.50). Find the critical angle for total internal reflection at the fibre-glass interface.
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a primary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a secondary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
