Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An optical fibre (μ = 1.72) is surrounded by a glass coating (μ = 1.50). Find the critical angle for total internal reflection at the fibre-glass interface.
Solution
Given,
Refractive index of the optical fibre is represented by μo = 1.72
Refractive index of glass coating is represented by μg= 1.50
Let the critical angle for glass be θc
Using the Snell's law,
\[\frac{\sin i}{\sin r} = \frac{\sin \theta_c}{\sin 90^\circ } = \frac{\mu_g}{\mu_0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\sin \theta_c}{\sin 90^\circ } = \frac{1 . 50}{1 . 72} = \frac{75}{86}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta_c = \sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{75}{86} \right)\]
Hence, the required critical angle is \[\sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{75}{86} \right)\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
A candle flame 1.6 cm high is imaged in a ball bearing of diameter 0.4 cm. If the ball bearing is 20 cm away from the flame, find the location and the height of the image.
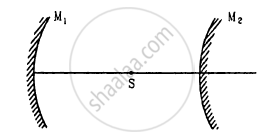
A converging mirror M1, a point source S and a diverging mirror M2 are arranged as shown in figure. The source is placed at a distance of 30 cm from M1. The focal length of each of the mirrors is 20 cm. Consider only the images formed by a maximum of two reflections. It is found that one image is formed on the source itself. (a) Find the distance between the two mirrors. (b) Find the location of the image formed by the single reflection from M2.
Light falls from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Find the angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is 90°.
A container contains water up to a height of 20 cm and there is a point source at the centre of the bottom of the container. A rubber ring of radius r floats centrally on the water. The ceiling of the room is 2.0 m above the water surface. (a) Find the radius of the shadow of the ring formed on the ceiling if r = 15 cm. (b) Find the maximum value of r for which the shadow of the ring is formed on the ceiling. Refractive index of water = 4/3.
A biconvex thick lens is constructed with glass (μ = 1.50). Each of the surfaces has a radius of 10 cm and the thickness at the middle is 5 cm. Locate the image of an object placed far away from the lens.
Answer the following question in detail.
State the conditions under which a rainbow can be seen.
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
Pick the wrong answer in the context with rainbow.
State any one difference between a primary rainbow and a secondary rainbow.
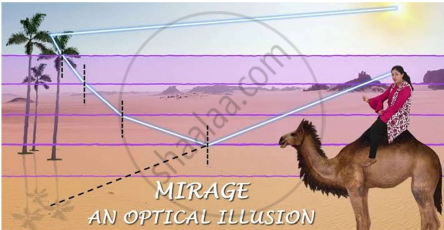
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
A diver at a depth 12 m inside water `(a_(µω) = 4/3)` sees the sky in a cone of semi-vertical angle
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
In an optical fibre, if n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, then which among the following, would be a correct equation?
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
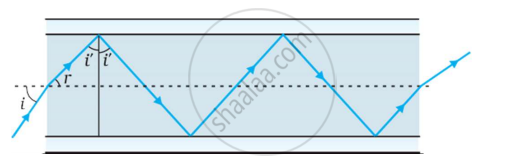
The following figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fiber of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for the following phenomena to occur.
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
