Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An optical fibre (μ = 1.72) is surrounded by a glass coating (μ = 1.50). Find the critical angle for total internal reflection at the fibre-glass interface.
उत्तर
Given,
Refractive index of the optical fibre is represented by μo = 1.72
Refractive index of glass coating is represented by μg= 1.50
Let the critical angle for glass be θc
Using the Snell's law,
\[\frac{\sin i}{\sin r} = \frac{\sin \theta_c}{\sin 90^\circ } = \frac{\mu_g}{\mu_0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\sin \theta_c}{\sin 90^\circ } = \frac{1 . 50}{1 . 72} = \frac{75}{86}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta_c = \sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{75}{86} \right)\]
Hence, the required critical angle is \[\sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{75}{86} \right)\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
Draw the intensity distribution for the diffraction bands produced due to single slit ?
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
The image formed by a concave mirror
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
A candle flame 1.6 cm high is imaged in a ball bearing of diameter 0.4 cm. If the ball bearing is 20 cm away from the flame, find the location and the height of the image.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.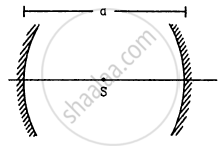
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
A paperweight in the form of a hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm is used to hold down a printed page. An observer looks at the page vertically through the paperweight. At what height above the page will the printed letters near the centre appear to the observer?
Explain: ‘How is a rainbow formed’?
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a secondary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
State any one difference between a primary rainbow and a secondary rainbow.
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is ______.
