Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
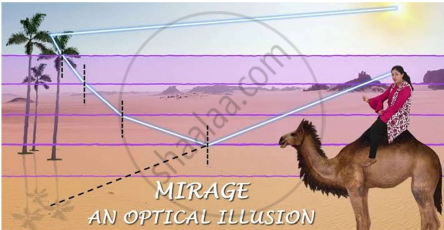 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
A diver at a depth 12 m inside water `(a_(µω) = 4/3)` sees the sky in a cone of semi-vertical angle
Options
`"sin"^-1 4/3`
`"tan"^-1 4/3`
`"sin"^-1 3 /4`
90°
Solution
`"sin"^-1(3/4)`
Explanation -
`"a"_(muω) = 1/("Sin" "C") => "Sin" "C" = 1/"a"_(µω) => "C" = "sin"^-1(1/"a"_(µω))`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Show with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised light from Sun gets linearly polarised by scattering.
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
What is linearly polarized light?
A 3 cm tall object is placed at a distance of 7.5 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 6 cm. Find the location, size and nature of the image.
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
Explain the formation of primary and secondary rainbow.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
In an optical fibre, if n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, then which among the following, would be a correct equation?
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because ______.
- light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
- there is no light scattered into this region.
- light is absorbed in this region.
- angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°.
