Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2021-2022
Date: April 2022
Duration: 2h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
- There are 12 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper has three sections: Section A, Section B and Section C.
- Section A contains three questions of two marks each, Section B contains eight questions of three marks each, and Section C contains one case study-based question of five marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks and two questions of three marks. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
- You may use log tables if necessary but use of calculator is not allowed.
In a pure semiconductor crystal of Si, if antimony is added then what type of extrinsic semiconductor is obtained. Draw the energy band diagram of this extrinsic semiconductor so formed.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Consider two different hydrogen atoms. The electron in each atom is in an excited state. Is it possible for the electrons to have different energies but same orbital angular momentum according to the Bohr model? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Explain how does (i) photoelectric current and (ii) kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in a photocell vary if the frequency of incident radiation is doubled, but keeping the intensity same?
Show the graphical variation in the above two cases.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Name the device which converts the change in intensity of illumination to change in electric current flowing through it. Plot I-V characteristics of this device for different intensities. State any two applications of this device.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Derive an expression for the frequency of radiation emitted when a hydrogen atom de-excites from level n to level (n – 1). Also show that for large values of n, this frequency equals to classical frequency of revolution of an electron.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Explain with a proper diagram how an ac signal can be converted into dc (pulsating) signal with output frequency as double than the input frequency using pn junction diode. Give its input and output waveforms.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
How long can an electric lamp of 100 W be kept glowing by fusion of 2 kg of deuterium? Take the fusion reaction as
\[\ce{^2_1H + ^2_1H -> ^3_2He + n + 3.27 MeV}\]
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Draw the shape of refracted wavefront when the plane incident wave undergoes refraction from optically denser medium to rarer medium. Hence prove Snell’s law of refraction.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Advertisements
Draw a ray diagram of compound microscope for the final image formed at least distance of distinct vision?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
An angular magnification of 30X is desired using an objective of focal length 1.25 cm and an eye piece of focal length 5 cm. How will you set up the compound microscope for the final image formed at least distance of distinct vision?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image formed at infinity
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5.0 cm. Find the magnifying power of the telescope for viewing distant objects when
- the telescope is in normal adjustment,
- the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Light of wavelength 2000 Å falls on a metal surface of work function 4.2 eV.
What is the kinetic energy (in eV) of the fastest electrons emitted from the surface?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Light of wavelength 2000 Å falls on a metal surface of work function 4.2 eV.
What will be the change in the energy of the emitted electrons if the intensity of light with same wavelength is doubled?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Light of wavelength 2000 Å falls on a metal surface of work function 4.2 eV.
If the same light falls on another surface of work function 6.5 eV, what will be the energy of emitted electrons?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Advertisements
Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of frequency of these waves.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
If the Earth did not have atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now? Explain.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
An e.m. wave exerts pressure on the surface on which it is incident. Justify.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
"If the slits in Young's double slit experiment are identical, then intensity at any point on the screen may vary between zero and four times to the intensity due to single slit".
Justify the above statement through a relevant mathematical expression.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Draw the intensity distribution as function of phase angle when diffraction of light takes place through coherently illuminated single slit.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
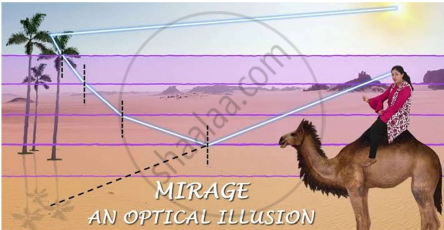
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
Which of the following phenomena is prominently involved in the formation of mirage in deserts?
Refraction, Total internal Reflection
Dispersion and Refraction
Dispersion and scattering of light
Total internal Reflection and diffraction
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
A diver at a depth 12 m inside water `(a_(µω) = 4/3)` sees the sky in a cone of semi-vertical angle
`"sin"^-1 4/3`
`"tan"^-1 4/3`
`"sin"^-1 3 /4`
90°
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
In an optical fibre, if n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, then which among the following, would be a correct equation?
n1 < n2
n1 = n2
n1 << n2
n1 > n2
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
A diamond is immersed in such a liquid which has its refractive index with respect to air as greater than the refractive index of water with respect to air. Then the critical angle of diamond-liquid interface as compared to critical angle of diamond-water interface will
depend on the nature of the liquid only
decrease
remain the same
increase
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
The following figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fiber of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for the following phenomena to occur.
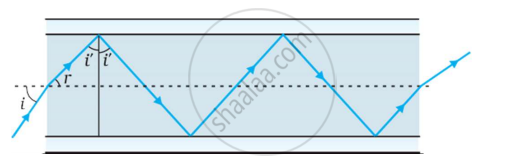
0 < i < 90°
0 < i < 60°
0 < i < 45°
0 < i < 30°
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2021 - 2022
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2022 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
