Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
Options
a convergent lens
a divergent lens
a rectangular slab
a prism.
Solution
a divergent lens
Since the refractive index of lens is less than that of of water and both the sides are convex, it will act like a normal diverging lens (though its focal length will change to negative).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Name the phenomenon responsible for it.
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
Suppose you are inside the water in a swimming pool near an edge. A friends is standing on the edge. Do you find your friend taller or shorter than his usual height?
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
A 1 cm object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 7.5 cm. Find its distance from the mirror if the image formed is 0.6 cm in size.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.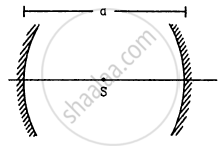
An optical fibre (μ = 1.72) is surrounded by a glass coating (μ = 1.50). Find the critical angle for total internal reflection at the fibre-glass interface.
A biconvex thick lens is constructed with glass (μ = 1.50). Each of the surfaces has a radius of 10 cm and the thickness at the middle is 5 cm. Locate the image of an object placed far away from the lens.
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
A paperweight in the form of a hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm is used to hold down a printed page. An observer looks at the page vertically through the paperweight. At what height above the page will the printed letters near the centre appear to the observer?
Answer the following question in detail.
State the conditions under which a rainbow can be seen.
Pick the wrong answer in the context with rainbow.
State any one difference between a primary rainbow and a secondary rainbow.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
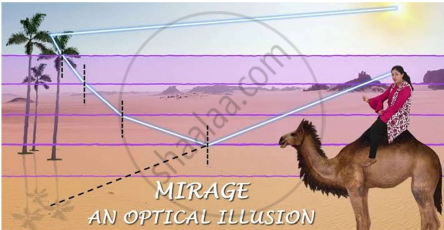 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
A diver at a depth 12 m inside water `(a_(µω) = 4/3)` sees the sky in a cone of semi-vertical angle
Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because ______.
- light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
- there is no light scattered into this region.
- light is absorbed in this region.
- angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°.
