Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A symmetric double convex lens in cut in two equal parts by a plane perpendicular to the principal axis. If the power of the original lens was 4 D, the power a cut-lens will be
Options
2 D
3 D
4 D
5 D.
Solution
2 D
The lens is cut into two equal parts by a plane perpendicular to the principal axis. Thus, the radius of curvature of both the lenses become half of its original value.
As,
\[f = \frac{R}{2}\]
\[P = \frac{1}{f}\]
Radius of curvature becomes half. Therefore, the focal also
reduces to half its original value.
Thus, the power (P) of the two cut-lenses will be equal.
2 P = 4 D
P = 2 D
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the power of a lens.
A student uses a lens of focal length 40 cm and another of –20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens
Give the usual name for the following:
A point inside a lens through which the light passes undeviated.
What is the power of a convex lens of focal length 0.5 m?
A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power, −1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
A convex lens of power 5 D and a concave lens of power 7.5 D are placed in contact with each other. What is the :
(a) power of this combination of lenses?
(b) focal length of this combination of lenses?
Name the type of lens whose power is positive.
The image of an object formed by a lens is real, inverted and of the same size as the object. If the image is at a distance of 40 cm from the lens, what is the nature and power of the lens ? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation `1/f =1/f_1 +1/f_2`for two thin lenses kept in contact coaxially.
A double convex lens has two surfaces of equal radii R and refractive index \[m = 1 \cdot 5\]
A screen is placed a distance 40 cm away from an illuminated object. A converging lens is placed between the source and the screen and its is attempted to form the image of the source on the screen. If no position could be found, the focal length of the lens
A double convex lens has focal length 25 cm. The radius of curvature of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
A 5.0 diopter lens forms a virtual image which is 4 times the object placed perpendicularly on the principal axis of the lens. Find the distance of the object from the lens.
The power of a lens is +2.0 D. Find its focal length and state the kind of lens.
A stick partly immersed in water appears to be bent. Draw a ray diagram to show the bending of the stick when placed in water and viewed obliquely from above.
If the lens is of focal length 25 cm. Calculate the power of the lens.
Focal length : metre : : power of lens : _______
Assertion and reasoning type
- Assertion: Myopia is due to the increase in the converging power of eye lens.
- Reason: Myopia can be corrected with the help of concave lens.

The above lens has a focal length of 10 cm. The object of height 2 mm is placed at a distance of 5 cm from the pole. Find the height of the image.
A point object is placed at O in front of a glass sphere as shown in figure.
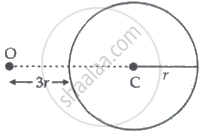
Show the formation of the image by the sphere.
An object is kept at a distance of 1m from a lens of power +2D:
- Identify the type of lens.
- Calculate its focal length and distance of the image formed.
