Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is ______.
Options
blue
green
violent
red
Solution
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is red.
Explanation:
As velocity of wave is given by the relation `v = f λ`. When light ray goes from one medium to other medium, the frequency of light remains unchanged. Hence `v oo λ` or greater the wavelength, greater the speed.
The light of red colour is of the highest wavelength and therefore of the highest speed. Therefore, after travelling through the slab, the red colour emerges first.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
The image formed by a concave mirror
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.50) to water (μ = 1.33). Find the range of the angle of deviation for which there are two angles of incidence.
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Explain: ‘How is a rainbow formed’?
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
Which of the following phenomena is prominently involved in the formation of mirage in deserts?
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
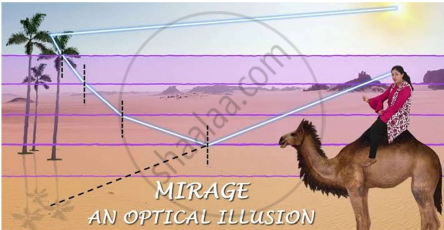 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
A diver at a depth 12 m inside water `(a_(µω) = 4/3)` sees the sky in a cone of semi-vertical angle
