Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
उत्तर
The effectiveness with which small particles scatter light depends on the size of the particles and the wavelength of the incident light. Red light has the longest wavelength and hence is scattered least by fog or smoke. Hence, red light can be clearly seen even from a distance. So, danger signal lights are usually red in colour.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
A candle flame 1.6 cm high is imaged in a ball bearing of diameter 0.4 cm. If the ball bearing is 20 cm away from the flame, find the location and the height of the image.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.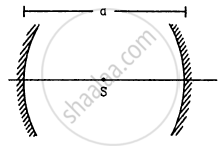
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

k transparent slabs are arranged one over another. The refractive indices of the slabs are μ1, μ2, μ3, ... μk and the thicknesses are t1 t2, t3, ... tk. An object is seen through this combination with nearly perpendicular light. Find the equivalent refractive index of the system which will allow the image to be formed at the same place.
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.50) to water (μ = 1.33). Find the range of the angle of deviation for which there are two angles of incidence.
A container contains water up to a height of 20 cm and there is a point source at the centre of the bottom of the container. A rubber ring of radius r floats centrally on the water. The ceiling of the room is 2.0 m above the water surface. (a) Find the radius of the shadow of the ring formed on the ceiling if r = 15 cm. (b) Find the maximum value of r for which the shadow of the ring is formed on the ceiling. Refractive index of water = 4/3.
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
A plano-convex lens is made of material having refractive index 1.5. The radius of curvature of curved surface is 40 cm. The focal length of the lens is ____________ cm.
Explain the formation of primary and secondary rainbow.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
Which of the following phenomena is prominently involved in the formation of mirage in deserts?
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
In an optical fibre, if n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, then which among the following, would be a correct equation?
