Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
उत्तर
Actual depth of the needle in water, h1 = 12.5 cm
Apparent depth of the needle in water, h2 = 9.4 cm
Refractive index of water = μ
The value of μ can be obtained as follows:
μ = `"h"_1/"h"_2`
= `12.5/9.4`
= 1.329 ≈ 1.33
Hence, the refractive index of water is about 1.33.
Water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index, μ' = 1.63
The actual depth of the needle remains the same, but its apparent depth changes. Let y be the new apparent depth of the needle. Hence, we can write the relation:
μ' = `"h"_1/"y"`
∴ y = `"h"_1/(μ"'")`
= `12.5/1.63`
= 7.67 cm
Hence, the new apparent depth of the needle is 7.67 cm. It is less than h2. Therefore, to focus the needle again, the microscope should be moved up.
∴ Distance by which the microscope should be moved up = 9.4 − 7.67 = 1.73 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
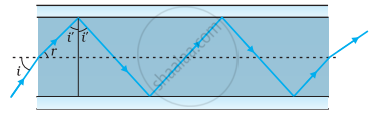
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.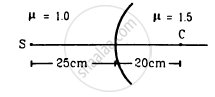
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
What is looming?
Write a note on optical fibre.
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
Show that for a material with refractive index `µ ≥ sqrt(2)`, light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
