Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
उत्तर
Refractive index of glass, μ = 1.55
Focal length of the double-convex lens, f = 20 cm
Radius of curvature of one face of the lens = R1
Radius of curvature of the other face of the lens = R2
Radius of curvature of the double-convex lens = R
∴ R1 = R and R2 = −R
The value of R can be calculated as:
`1/"f" = (μ - 1)[1/"R"_1 - 1/"R"_2]`
`1/20 = (1.55 - 1)[1/"R" + 1/"R"]`
`1/20 = 0.55 xx 2/"R"`
R = 0.55 × 2 × 20
∴ R = 22 cm
Hence, the radius of curvature of the double-convex lens is 22 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is?
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.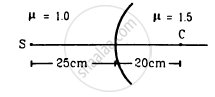
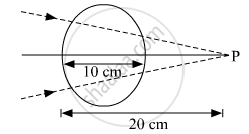
A converging beam of light traveling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1⋅5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of, the image. Also, draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
What is looming?
What is Snell’s window?
Write a note on optical fibre.
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
A light travels through water in the beaker. The height of water column is 'h'. Refractive index of water is 'μw'. If c is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will ______.
The critical angle is maximum when light travels from ______.
`(a^mu"w"=4/3,a^mug=3/2)`
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
