Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
उत्तर
Actual depth of the pin, d = 15 cm
Apparent depth of the pin = d'
Refractive index of glass, μ = 1.5
Ratio of actual depth to the apparent depth is equal to the refractive index of glass, i.e.
`μ = "d"/"d'"`
∴ d' = `"d"/μ`
= `15/1.5`
= 10 cm
The distance at which the pin appears to be raised = d' − d = 15 − 10 = 5 cm
For a small angle of incidence, this distance does not depend upon the location of the slab.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
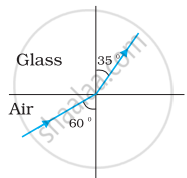
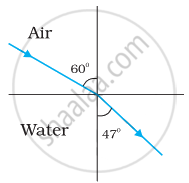
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
 |
 |
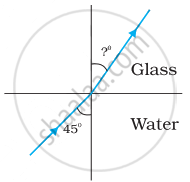 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
Stars twinkle due to ______.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
What is a principle of reversibility?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Write a short note on the prisms making use of total internal reflection.
How does an endoscope work?
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
A light travels through water in the beaker. The height of water column is 'h'. Refractive index of water is 'μw'. If c is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will ______.
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
