Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
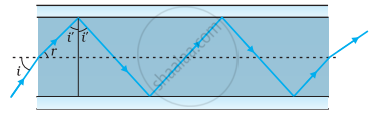
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
उत्तर
(a) Refractive index of the glass fibre, μ1 = 1.68
Refractive index of the outer covering of the pipe, μ2 = 1.44
Angle of incidence = i
Angle of refraction = r
Angle of incidence at the interface = i'
The refractive index (μ) of the inner core − outer core interface is given as:
`μ = μ_2/μ_1 = 1/(sin "i'")`
`sin "i'" = (μ_1)/(μ_2)`
= `1.44/1.68`
= 0.8571
∴ i' = 59°
For the critical angle, total internal reflection (TIR) takes place only when i > i', i.e., i > 59°
Maximum angle of reflection, rmax = 90° − i' = 90° − 59° = 31°
Let, imax be the maximum angle of incidence.
The refractive index at the air-glass interface, μ1 = 1.68
We have the relation for the maximum angles of incidence and reflection as:
`μ_1 = (sin "i"_"max")/sin "r"_"max"`
sin imax = μ1 sin rmax
= 1.68 sin 31°
= 1.68 × 0.5150
= 0.8652
∴ imax = sin−1 0.8652 ≈ 60°
Thus, all the rays incident at angles lying in the range 0 < i < 60° will suffer total internal reflection
(b) If the outer covering of the pipe is not present, then:
Refractive index of the outer pipe, μ1 = Refractive index of air = 1
For the angle of incidence i = 90°, we can write Snell’s law at the air − pipe interface as:
`sin "i"/sin "r" = μ_2` = 1.68
`sin "r" = (sin 90°)/1.68 = 1/1.68`
`"r" = sin^(-1) (0.5952)`
= 36.5°
∴ i' = 90° − 36.5° = 53.5°
Since i' > r, all incident rays will suffer total internal reflection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
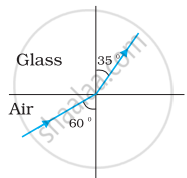
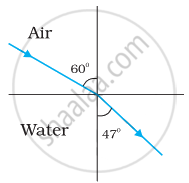
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
 |
 |
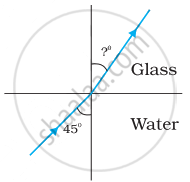 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is a principle of reversibility?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
Write a note on optical fibre.
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
When a ray of light is refracted from one medium to another, then the wavelength changes from 6000Å to 4000Å. The critical angle for the interface will be ______.
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
Light travels in two media A and B with speeds 1.8 × 108 ms−1 and 2.4 × 108 ms−1 respectively. Then the critical angle between them is:
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?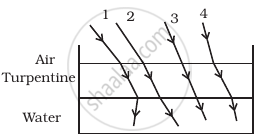
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
