Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
पर्याय
infinity
pole
focus
15 cm behind the mirror.
उत्तर
15 cm behind the mirror
Since u = − 30 cm
v = ?
f = 30 cm
From the mirror formula
\[\frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[or\frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{f} - \frac{1}{u}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{30} - \frac{1}{- 30}\]
\[\frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{30} + \frac{1}{30}\]
\[\frac{1}{v} = \frac{2}{30}\]
\[ \therefore v = 15 \text{ cm }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
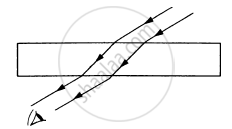
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is μ. (a) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye? (b) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the image(s) of the fish.

Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Stars twinkle due to ______.
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
What is mirage?
Write a short note on the prisms making use of total internal reflection.
What is Snell’s window?
How does an endoscope work?
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
