Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
Solution
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
When the light strikes on a surface nearly parallel to it, it then bends by a small and fixed angle after reflection. Also, when the light travels from one medium to another with slight differences in their refractive indices, it bends by a small angle. Thus, the bending of light by a small but fixed angle can be the case of either reflection or refraction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backward as shown in Figure. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5° of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?

Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
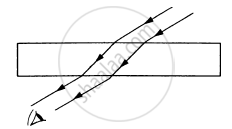
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

Choose the correct option.
There are different fish, monkeys, and water of the habitable planet of the star Proxima b. A fish swimming underwater feels that there is a monkey at 2.5 m on the top of a tree. The same monkey feels that the fish is 1.6 m below the water surface. Interestingly, height of the tree and the depth at which the fish is swimming are exactly same. Refractive index of that water must be
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
What is mirage?
Write a short note on the prisms making use of total internal reflection.
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
When a ray of light is refracted from one medium to another, then the wavelength changes from 6000Å to 4000Å. The critical angle for the interface will be ______.
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
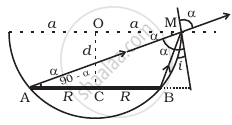
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?