Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

Solution
Given,
The radius of the transparent hemisphere (R) = 3.0 cm
Refractive index of the material (μ2) = 2.0
Let the critical angle be θc
∴ critical angle is given by θc = \[\sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{1}{\mu_2} \right) = \sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{1}{2} \right) = 30^\circ\]
(a)
From the figure it is seen that the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, so the rays are totally reflected at the plane surface.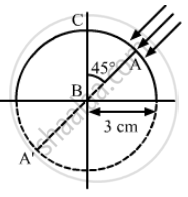
(b) Using the lens equation:
\[\frac{\mu_2}{v} - \frac{\mu_1}{u} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{2}{v} - \left( - \frac{1}{\infty} \right) = \frac{2 - 1}{3} (\text{ for parallel rays u = \infty })\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{2}{v} = \frac{1}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = 6 cm\]
If we complete the sphere then the image will be formed diametrically opposite to A.
(c)
By internal reflection, the image is formed in front of A.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
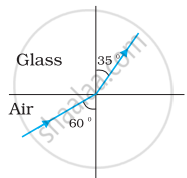 |
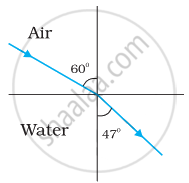 |
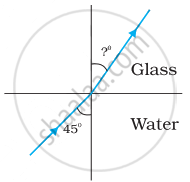 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
The refractive index of diamond is much greater than that of ordinary glass. Is this fact of some use to a diamond cutter?
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is a principle of reversibility?
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
The critical angle is maximum when light travels from ______.
`(a^mu"w"=4/3,a^mug=3/2)`
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
Light travels in two media A and B with speeds 1.8 × 108 ms−1 and 2.4 × 108 ms−1 respectively. Then the critical angle between them is:
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is `h/3`. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
