Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A and B with refractive indices 1.33 and 1.48 respectively. The medium A is on the convex side of the surface. Where should a point object be placed in medium A so that the paraxial rays become parallel after refraction at the surface?
Solution
Given,
Spherical surface of radius (R) = 30 cm
Medium A has refractive index (μ1) = 1.33
Medium B has refractive index (μ2) = 1.48
Medium A is the convex side of surface.
Since,
We know that paraxial rays become parallel after refraction
i.e, the image of the point object will be formed at infinity.
Therefore v = ∞
Using the lens equation,
\[\frac{\mu_2}{v} - \frac{\mu_1}{u} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1 . 48}{\infty} - \frac{1 . 33}{u} = \frac{1 . 48 - 1 . 33}{30}\]
\[ \Rightarrow - \frac{1 . 33}{u} - \frac{0 . 15}{30}\]
\[ \therefore u = - 266 . 0 cm\]
Hence, the object is placed at a distance of 266.0 cm from the convex surface on side A.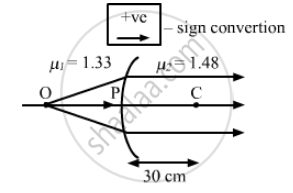
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
If an object far away from a convex mirror moves towards the mirror, the image also moves. Does it move faster, slower or at the same speed as compared to the object?
Can mirrors give rise to chromatic aberration?
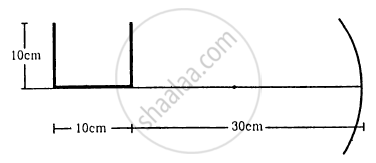
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
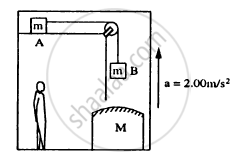
Consider the situation shown in figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration of 2.00 m s−2 and the focal length of the mirror is 12.0 cm. All the surfaces are smooth and the pulley is light. The mass-pulley system is released from rest (with respect to the elevator) at t = 0 when the distance of B from the mirror is 42.0 cm. Find the distance between the image of the block B and the mirror at t = 0.200 s. Take g = 10 m s−2.
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
How can the spherical aberration produced by a lens be minimized?
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
Focal length of a mirror is given by ______.
A thin converging lens of focal length 12 cm is kept in contact with a thin diverging lens of focal length 18 cm. Calculate the effective/equivalent focal length of the combination.
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
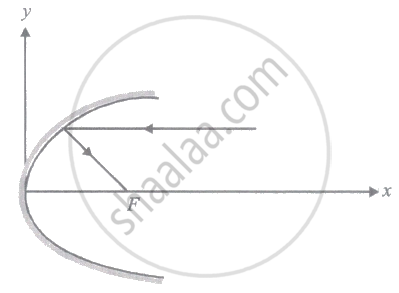
A parallel beam of light ray parallel to the x-axis is incident on a parabolic reflecting surface x = 2by2 as shown in the figure. After reflecting it passes through focal point F. What is the focal length of the reflecting surface?
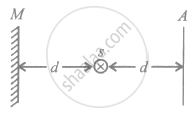
The intensity of a point source of light, S, placed at a distance d in front of a screen A, is I0 at the center of the screen. Find the light intensity at the center of the screen if a completely reflecting plane mirror M is placed at a distance d behind the source, as shown in the figure.
A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object placed at (– 50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
An object is 20 cm away from a concave mirror and it is within the focal length of the mirror. If the mirror is changed to a plane mirror, the image moves 15 cm closer to the mirror.
Focal length of the concave mirror is ______.
A converging lens has a focal length of 10 cm in air. It is made of a material with a refractive index of 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3, find its new focal length.
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
