Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
Solution
Size of the candle, h = 2.5 cm
Image size = h'
Object distance, u = −27 cm
Radius of curvature of the concave mirror, R = −36 cm
Focal length of the concave mirror, f = `"R"/2 = (-36)/2` = −18 cm
Image distance = v
The image distance can be obtained using the mirror formula:
`1/"u" + 1/"v" = 1/"f"`
`1/"v" = 1/"f" - 1/"u"`
= `1/-18 - 1/-27`
= `(-3 + 2)/54`
= `-1/54`
∴ v = −54 cm
Therefore, the screen should be placed 54 cm away from the mirror to obtain a sharp image.
The magnification of the image is given as:
`"m" = "h'"/"h" = - "v"/"u"`
∴ h' = `-"v"/"u" xx "h"`
= `-(-54)/(-27) xx 2.5`
= −5 cm
The height of the candle’s image is 5 cm. The negative sign indicates that the image is inverted and real.
If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, then the screen will have to be moved away from the mirror in order to obtain the image.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can mirrors give rise to chromatic aberration?
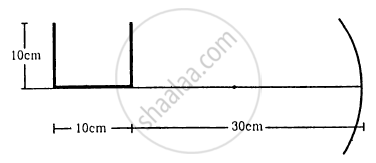
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
A man uses a concave mirror for shaving. He keeps his face at a distance of 25 cm from the mirror and gets an image which is 1.4 times enlarged. Find the focal length of the mirror.
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A and B with refractive indices 1.33 and 1.48 respectively. The medium A is on the convex side of the surface. Where should a point object be placed in medium A so that the paraxial rays become parallel after refraction at the surface?
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
A converging lens and a diverging mirror are placed at a separation of 15 cm. The focal length of the lens is 25 cm and that of the mirror is 40 cm. Where should a point source be placed between the lens and the mirror so that the light, after getting reflected by the mirror and then getting transmitted by the lens, comes out parallel to the principal axis?
How can the spherical aberration produced by a lens be minimized?
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

Answer the following question.
With the help of a ray diagram, obtain the relation between its focal length and radius of curvature.
According to the mirror equation, ______.
A thin converging lens of focal length 12 cm is kept in contact with a thin diverging lens of focal length 18 cm. Calculate the effective/equivalent focal length of the combination.
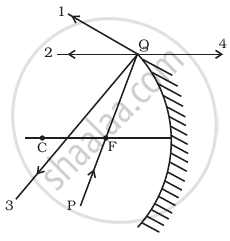
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h–1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20 m and an eyepiece of focal length 2 cm.
- The length of the telescope tube is 20.02 m.
- The magnification is 1000.
- The image formed is inverted.
- An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the image.
A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f, what will be the length of the image? You may take L << |v – f|.
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
A converging lens has a focal length of 10 cm in air. It is made of a material with a refractive index of 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3, find its new focal length.
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
