Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f, what will be the length of the image? You may take L << |v – f|.
Solution
As the mean distance of object from mirror is u
∴ `u_1 = u - L/2` and `u_2 = (u + L/2)`
Let the image of the two ends of object form at distance v1 and v2(v1 > v2). So length of image on principal axis is L' = (v1 – v2)
`1/v + 1/u = 1/f` or `1/v + 1/f = 1/u`
⇒ `1/v = (u - f)/(uf)`
⇒ `v = (uf)/(u - f)`
So L' = `v_1 - v_2 = ((u - L/2)f)/((u - L/2) - f) - ((u + L/2)f)/((u + L/2) - f)`
⇒ L' = `f (u - L/2)/((u - f - L/2)) - (u + 1/2)/((u - f + L/2))`
⇒ L' = `f[((u - L/2)(u - f + L/2) - (u + L/2)(u - f - L/2))/((u - f - L/2)(u - f + 1/2))]`
= `(f[u^2 - uf + (uL)/2 - (uL)/2 + (fL)/2 - L^2/4 - (u^2 - uf - (uL)/2 + (uL)/2 - (fL)/2 - L^2/4)])/((u - f)^2 - L^2/4)`
∴ `L < < (u - f)`
∴ `L^2/4 < < < (u - f)`
So neglecting the terms `L^2/4`
`L^2 = f[((fL)/2 + (fL)/2)/(u - f)^2]`
`L^2 = (ffL)/((u - f)^2` ⇒ `L^2 = (Lf^2)/((u - f)^2`
It is the length of image f.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If an object far away from a convex mirror moves towards the mirror, the image also moves. Does it move faster, slower or at the same speed as compared to the object?
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
A narrow pencil of parallel light is incident normally on a solid transparent sphere of radius r. What should be the refractive index is the pencil is to be focussed (a) at the surface of the sphere, (b) at the centre of the sphere.
Two thin lenses having optical powers of -10D and+ 6D are placed in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is:
State how the focal length of a glass lens (Refractive Index 1.5) changes when it is completely immersed in:
(i) Water (Refractive Index 1.33)
(ii) A liquid (Refractive Index 1.65)
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will ______.
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
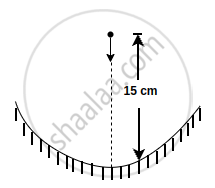
A particle is dropped along the axis from a height 15 cm on a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm as shown in figure. The acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2. Find the maximum speed of image in m/s: