Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
With the help of a ray diagram, obtain the relation between its focal length and radius of curvature.
Solution
The distance between the centre of a lens or curved mirror and its focus.
The relationship between the focal length f and the radius of curvature R = 2f.

Consider a ray of light AB, parallel to the principal axis and incident on a spherical mirror at point B. The normal to the surface at point B is CB and CP = CB = R is the radius of curvature. The ray AB, after reflection from a mirror, will pass through F (concave mirror) or will appear to diverge from F (convex mirror) and obeys the law of reflection i.e. i = r.
From the geometry of the figure,
∠BCP = θ = i
In D CBF, θ = r
∴BF = FC (because i = r)
If the aperture of the mirror is small, B lies close to P, and therefore BF = PF
Or FC = FP = PF
Or PC = PF + FC = PF + PF
Or R = 2 PF = 2f
Or f = R/2
Similar relation holds for convex mirror also. In deriving this relation, we have assumed that the aperture of the mirror is small.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can mirrors give rise to chromatic aberration?
A man uses a concave mirror for shaving. He keeps his face at a distance of 25 cm from the mirror and gets an image which is 1.4 times enlarged. Find the focal length of the mirror.
A converging lens and a diverging mirror are placed at a separation of 15 cm. The focal length of the lens is 25 cm and that of the mirror is 40 cm. Where should a point source be placed between the lens and the mirror so that the light, after getting reflected by the mirror and then getting transmitted by the lens, comes out parallel to the principal axis?
According to Cartesian sign convention, all distances are measured from the _______.
According to the mirror equation, ______.
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will ______.
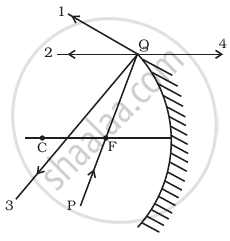
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20 m and an eyepiece of focal length 2 cm.
- The length of the telescope tube is 20.02 m.
- The magnification is 1000.
- The image formed is inverted.
- An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the image.
An object is 20 cm away from a concave mirror and it is within the focal length of the mirror. If the mirror is changed to a plane mirror, the image moves 15 cm closer to the mirror.
Focal length of the concave mirror is ______.
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
