Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How can the spherical aberration produced by a lens be minimized?
Solution
In order to remove the spherical aberration, the central part of the lens is covered with an opaque object called a stop.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
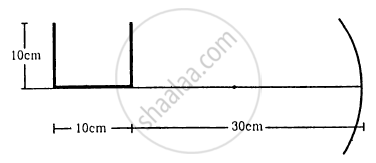
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
A narrow pencil of parallel light is incident normally on a solid transparent sphere of radius r. What should be the refractive index is the pencil is to be focussed (a) at the surface of the sphere, (b) at the centre of the sphere.
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
According to Cartesian sign convention, all distances are measured from the _______.
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
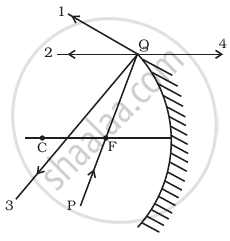
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f, what will be the length of the image? You may take L << |v – f|.
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
