Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The refractive index of diamond is much greater than that of ordinary glass. Is this fact of some use to a diamond cutter?
Solution
Yes
The refractive index of diamond (2.42) is more than that of ordinary glass (1.5). The critical angle for diamond is less than that for glass. A diamond cutter uses a large angle of incidence to ensure that the light entering the diamond is totally reflected from its face. This is the reason for the sparkling effect of a diamond.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
A laser light is focussed by a converging lens. Will there be a significant chromatic aberration?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is μ. (a) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye? (b) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the image(s) of the fish.

A point ‘O’ marked on the surface of a glass sphere of diameter 20 cm is viewed through glass from the position directly opposite to the point O. If the refractive index of the glass is 1.5, find the position of the image formed. Also, draw the ray diagram for the formation of the image.
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
What is relative refractive index?
How does an endoscope work?
Derive the equation for acceptance angle and numerical aperture, of optical fiber.
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
When a ray of light is refracted from one medium to another, then the wavelength changes from 6000Å to 4000Å. The critical angle for the interface will be ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?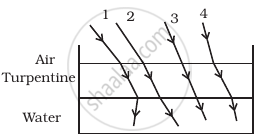
A convex lens made of material of refractive index 1.5 and having a focal length of 10 cm is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 3.0. The lens will behave as ______.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
