Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
 |
 |
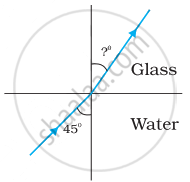 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
Solution
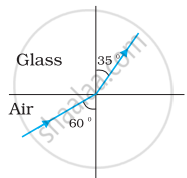
As per the given figure, for the glass-air interface:
Angle of incidence, i = 60°
Angle of refraction, r = 35°
The relative refractive index of glass with respect to air is given by Snell’s law as:
`""^"a"μ_"g" = (sin "i")/(sin "r")`
= `(sin 60°)/(sin 35°)`
= `(0.8660)/(0.5736)`
= 1.51 ......(1)
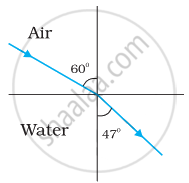
As per the given figure, for the air-water interface:
Angle of incidence, i = 60°
Angle of refraction, r = 47°
The relative refractive index of water with respect to air is given by Snell’s law as:
`""^"a"μ_"w" = (sin "i")/(sin "r")`
= `(sin 60°)/(sin 47°)`
= `(0.8660)/(0.7314)`
= 1.184 ....(2)
Using (1) and (2), the relative refractive index of glass with respect to water can be obtained as:
`""^"w"μ_"g" = (""^"a"μ_"g")/(""^"a"μ_"w")`
= `1.51/1.184`
= 1.275
The following figure shows the situation involving the glass-water interface.
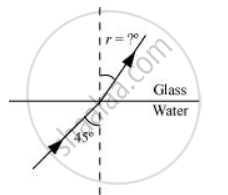
Angle of incidence, i = 45°
Angle of refraction = r
From Snell’s law, r can be calculated as:
`(sin "i")/(sin "r") = ""^"w"μ_"g"`
`(sin 45°)/sin "r"` = 1.275
sin r = `(1/(sqrt2))/1.275`
sin r = 0.5546
∴ r = `sin^(-1) (0.5546)` = 33.68°
Hence, the angle of refraction at the water-glass interface is 33.68°.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is?
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
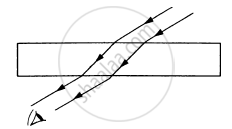
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
Choose the correct option.
There are different fish, monkeys, and water of the habitable planet of the star Proxima b. A fish swimming underwater feels that there is a monkey at 2.5 m on the top of a tree. The same monkey feels that the fish is 1.6 m below the water surface. Interestingly, height of the tree and the depth at which the fish is swimming are exactly same. Refractive index of that water must be
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Why do stars twinkle?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
