Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
उत्तर
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
When the light strikes on a surface nearly parallel to it, it then bends by a small and fixed angle after reflection. Also, when the light travels from one medium to another with slight differences in their refractive indices, it bends by a small angle. Thus, the bending of light by a small but fixed angle can be the case of either reflection or refraction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1·6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1·3, find its new focal length.
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

A point ‘O’ marked on the surface of a glass sphere of diameter 20 cm is viewed through glass from the position directly opposite to the point O. If the refractive index of the glass is 1.5, find the position of the image formed. Also, draw the ray diagram for the formation of the image.
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
Write a note on optical fibre.
Derive the equation for acceptance angle and numerical aperture, of optical fiber.
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
The critical angle is maximum when light travels from ______.
`(a^mu"w"=4/3,a^mug=3/2)`
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?
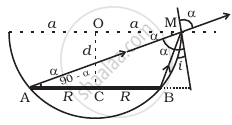
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
