Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The rays of different colours fail to converge at a point after going through a converging lens. This defect is called
विकल्प
spherical aberration
distortion
coma
chromatic aberration.
उत्तर
chromatic aberration
When light rays of different colours do not converge at the same point after passing through a converging lens, it is called chromatic aberration. This happens because a lens has different refractive indices for different colours, i.e, for different wavelengths of light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.
Use the mirror equation to show that a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
Define the term 'limit of resolution'?
Use the mirror equation to show a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object ?
Can a plane mirror ever form a real image?
following Figure shows two rays A and B being reflected by a mirror and going as A' and B'. The mirror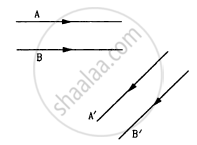
Mark the correct options.
A light ray falling at an angle of 45° with the surface of a clean slab of ice of thickness 1.00 m is refracted into it at an angle of 30°. Calculate the time taken by the light rays to cross the slab. Speed of light in vacuum = 3 × 108 m s−1.
A cylindrical vessel of diameter 12 cm contains 800π cm3 of water. A cylindrical glass piece of diameter 8.0 cm and height 8.0 cm is placed in the vessel. If the bottom of the vessel under the glass piece is seen by the paraxial rays (see figure), locate its image. The index of refraction of glass is 1.50 and that of water is 1.33.

A light ray is incident at an angle of 45° with the normal to a √2 cm thick plate (μ = 2.0). Find the shift in the path of the light as it emerges out from the plate.
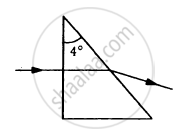
Find the angle of deviation suffered by the light ray shown in figure. The refractive index μ = 1.5 for the prism material.
Write any one use for each of the following mirrors :
(a) Convex
(b) Concave
Name the physical principle on which the working of optical fibers is based.
For paraxial rays, show that the focal length of a spherical mirror is one-half of its radius of curvature.
A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a transparent spherical globe of diameter 30cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance from the centre of the globe at which the beam of light can converge is ______ mm.
Car B overtakes car A at a relative speed of 40 ms-1. How fast will the image of car B appear to move in the mirror of focal length 10 cm fitted in car A, when car B is 1.9 m away from car A?
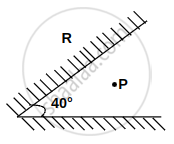
Two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle of 40°. The possible number of images of an object placed at point P would be?