Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
उत्तर
- The diamond appears dazzling because the total internal reflection of light happens inside the diamond.
- The refractive index of only diamonds is about 2.417. It is much larger than that for ordinary glass which is about only 1.5.
- The critical angle of a diamond is about 24.4°. It is much less than that of glass.
- A skilled diamond cutter makes use of this larger range of angle of incidence (24.4° to 90° inside the diamond), to ensure that light entering the diamond is total internally reflected from the many cut faces before getting out.
- This gives a sparkling effect for diamond.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1·6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1·3, find its new focal length.
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
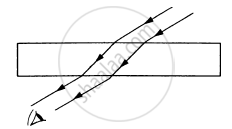
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
A converging beam of light travelling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1 . 5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of the image. Also draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
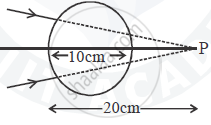
A converging beam of light traveling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1⋅5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of, the image. Also, draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
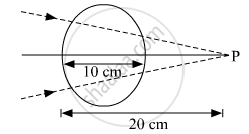
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
Write a note on optical fibre.
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
