Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two identical circular coils, P and Q each of radius R, carrying currents 1 A and √3A respectively, are placed concentrically and perpendicular to each other lying in the XY and YZ planes. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the centre of the coils.
उत्तर

Magentic field at the centre of the coil are perpendicular to each other. Therefore net magnetic field (B) is the resultant of the two fields caused due to coil P and Q, respectively.
`B_P = (μ_oI)/(2πR)= (μ_o)/(2πR)`
`B_Q= (μ_oI)/(2πR)= (μ_osqrt3)/(2πR)`
Net magnetic field, `B = sqrt(B_P^2 + B_Q^2)`
`=sqrt((μ_o/(2πR))^2 + ( (μ_osqrt3)/(2πR))^2) `
`= μ_o/(2πR)sqrt4`
`= μ_o/(πR)`
For direction of net magnetic field
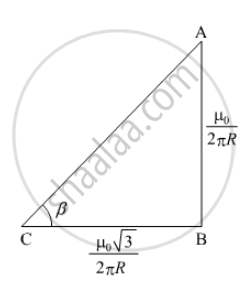
`tanβ =(AB)/(BC)`
`= (μ_o/(2πR))/((μ_osqrt3)/(2πR)) = 1/sqrt3`
`β= 30^@`
The direction of net magnetic field is 30° with the X-direction.
संबंधित प्रश्न
At a place, the horizontal component of earth's magnetic field is B and angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field at equator?
A circular loop is kept in that vertical plane which contains the north-south direction. It carries a current that is towards north at the topmost point. Let A be a point on the axis of the circle to the east of it and B a point on this axis to the west of it. The magnetic field due to the loop
Two circular coils of radii 5.0 cm and 10 cm carry equal currents of 2.0 A. The coils have 50 and 100 turns respectively and are placed in such a way that their planes as well as the centres coincide. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the common centre of the coils if the currents in the coils are (a) in the same sense (b) in the opposite sense.
A circular loop of radius 20 cm carries a current of 10 A. An electron crosses the plane of the loop with a speed of 2.0 × 106 m s−1. The direction of motion makes an angle of 30° with the axis of the circle and passes through its centre. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron at the instant it crosses the plane.
A piece of wire carrying a current of 6.00 A is bent in the form of a circular are of radius 10.0 cm, and it subtends an angle of 120° at the centre. Find the magnetic field B due to this piece of wire at the centre.
A charge of 3.14 × 10−6 C is distributed uniformly over a circular ring of radius 20.0 cm. The ring rotates about its axis with an angular velocity of 60.0 rad s−1. Find the ratio of the electric field to the magnetic field at a point on the axis at a distance of 5.00 cm from the centre.
The magnetic field at a distance r from a long wire carrying current I is 0.4 tesla. The magnetic field at a distance 2 r is ______.
A small square loop of wire of side l is placed inside a large square loop of side L (L >> l). The loop is coplanar and their centers coincide. The mutual inductance of the system is proportional to is
An electron is projected along the axis of a circular conductor carrying some current. Electron ______
Two horizontal thin long parallel wires, separated by a distance r carry current I each in the opposite directions. The net magnetic field at a point midway between them will be ______.
