Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
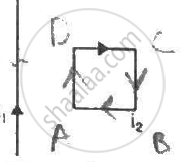
A circular loop is kept in that vertical plane which contains the north-south direction. It carries a current that is towards north at the topmost point. Let A be a point on the axis of the circle to the east of it and B a point on this axis to the west of it. The magnetic field due to the loop
विकल्प
is towards east at A and towards west at B
is towards west at A and towards east at B
is towards east at both A and B
is towards west at both A and B
उत्तर
is towards west at both A and B
According to the right-hand thumb rule, if we curl the fingers of our right hand in the direction of the current flowing, then the stretching of the thumb will show the direction of the magnetic field developed due to it and vice versa.
Let north-south is along x axis and east-west is along y axis. Circular wire is in xz plane. Then point A will lie on positive y axis and B on negative y axis. On looking from point B, current is flowing in anticlockwise direction so the magnetic field will point from right to left. Hence, the magnetic field due to the loop will be towards west at both A and B.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use Biot-Savart law to derive the expression for the magnetic field on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius R.
Draw the magnetic field lines due to a circular wire carrying current I.
Two concentric circular coils X and Y of radii 16 cm and 10 cm, respectively, lie in the same vertical plane containing the north to south direction. Coil X has 20 turns and carries a current of 16 A; coil Y has 25 turns and carries a current of 18 A. The sense of the current in X is anticlockwise, and clockwise in Y, for an observer looking at the coils facing west. Give the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field due to the coils at their centre.
Two identical circular coils, P and Q each of radius R, carrying currents 1 A and √3A respectively, are placed concentrically and perpendicular to each other lying in the XY and YZ planes. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the centre of the coils.
A current-carrying, straight wire is kept along the axis of a circular loop carrying a current. This straight wire
Consider the situation shown in figure. The straight wire is fixed but the loop can move under magnetic force. The loop will
A steady electric current is flowing through a cylindrical conductor.
(a) The electric field at the axis of the conductor is zero.
(b) The magnetic field at the axis of the conductor is zero.
(c) The electric field in the vicinity of the conductor is zero.
(d) The magnetic field in the vicinity of the conductor is zero.
A circular loop of radius 20 cm carries a current of 10 A. An electron crosses the plane of the loop with a speed of 2.0 × 106 m s−1. The direction of motion makes an angle of 30° with the axis of the circle and passes through its centre. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron at the instant it crosses the plane.
A circular loop of radius R carries a current I. Another circular loop of radius r(<<R) carries a current i and is placed at the centre of the larger loop. The planes of the two circles are at right angle to each other. Find the torque acting on the smaller loop.
A piece of wire carrying a current of 6.00 A is bent in the form of a circular are of radius 10.0 cm, and it subtends an angle of 120° at the centre. Find the magnetic field B due to this piece of wire at the centre.
A circular coil of 200 turns has a radius of 10 cm and carries a current of 2.0 A. (a) Find the magnitude of the magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] at the centre of the coil. (b) At what distance from the centre along the axis of the coil will the field B drop to half its value at the centre?
Which of these equations is the correct expression for force on a charge in magnetic field?
The magnitude of the magnetic field due to a circular coil of radius R carrying a current I at an axial distance x from the centre is ______.
The magnetic field at a distance r from a long wire carrying current I is 0.4 tesla. The magnetic field at a distance 2 r is ______.
If we double the radius of a coil keeping the current through it unchanged, then the magnetic field at any point at a large distance from the centre becomes approximately.
A small square loop of wire of side l is placed inside a large square loop of side L (L >> l). The loop is coplanar and their centers coincide. The mutual inductance of the system is proportional to is
Consider a circular current-carrying loop of radius R in the x-y plane with centre at origin. Consider the line intergral
`ℑ(L ) = |int_(-L)^L B.dl|` taken along z-axis.
- Show that ℑ(L) monotonically increases with L.
- Use an appropriate Amperian loop to show that ℑ(∞) = µ0I, where I is the current in the wire.
- Verify directly the above result.
- Suppose we replace the circular coil by a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about ℑ(L) and ℑ(∞)?
The fractional change in the magnetic field intensity at a distance 'r' from centre on the axis of the current-carrying coil of radius 'a' to the magnetic field intensity at the centre of the same coil is ______.
(Take r < a).
Two horizontal thin long parallel wires, separated by a distance r carry current I each in the opposite directions. The net magnetic field at a point midway between them will be ______.
