Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A circular loop of radius R carries a current I. Another circular loop of radius r(<<R) carries a current i and is placed at the centre of the larger loop. The planes of the two circles are at right angle to each other. Find the torque acting on the smaller loop.
उत्तर
Given:
For the outer loop,
Magnitude of current = I
Radius of the loop = R
Thus, the magnetic field at the centre due to the larger loop is given by
Now,
Angle between the area vector of the smaller loop and the magnetic field due to the larger loop = 90°
Thus, the required torque is given by
= iABsin 90°
\[= i\pi r^2 \frac{\mu_0 I}{2R}\]
\[ = \frac{\mu_0 \pi r^2 Ii}{2R}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A circular loop is kept in that vertical plane which contains the north-south direction. It carries a current that is towards north at the topmost point. Let A be a point on the axis of the circle to the east of it and B a point on this axis to the west of it. The magnetic field due to the loop
Consider the situation shown in figure. The straight wire is fixed but the loop can move under magnetic force. The loop will
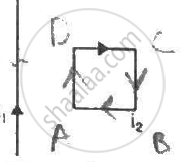
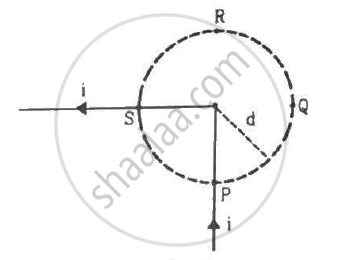
Figure shows a long wire bent at the middle to form a right angle. Show that the magnitudes of the magnetic fields at the point P, Q, R and S are equal and find this magnitude.
Two circular coils of radii 5.0 cm and 10 cm carry equal currents of 2.0 A. The coils have 50 and 100 turns respectively and are placed in such a way that their planes as well as the centres coincide. If the outer coil is rotated through 90° about a diameter, Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the common centre of the coils if the currents in the coils are (a) in the same sense (b) in the opposite sense.
A circular loop of radius r carrying a current i is held at the centre of another circular loop of radius R(>>r) carrying a current I. The plane of the smaller loop makes an angle of 30° with that of the larger loop. If the smaller loop is held fixed in this position by applying a single force at a point on its periphery, what would be the minimum magnitude of this force?
Find the magnetic field B due to a semicircular wire of radius 10.0 cm carrying a current of 5.0 A at its centre of curvature.
A circular loop of radius r carries a current i. How should a long, straight wire carrying a current 4i be placed in the plane of the circle so that the magnetic field at the centre becomes zero?
Which of these equations is the correct expression for force on a charge in magnetic field?
The magnitude of the magnetic field due to a circular coil of radius R carrying a current I at an axial distance x from the centre is ______.
The magnetic field at a distance r from a long wire carrying current I is 0.4 tesla. The magnetic field at a distance 2 r is ______.
A charged particle moving in a uniform magnetic field and losses 4% of its kinetic energy. The radius of curvature of its path changes by ______.
A small square loop of wire of side l is placed inside a large square loop of side L (L >> l). The loop is coplanar and their centers coincide. The mutual inductance of the system is proportional to is
The fractional change in the magnetic field intensity at a distance 'r' from centre on the axis of the current-carrying coil of radius 'a' to the magnetic field intensity at the centre of the same coil is ______.
(Take r < a).
Two horizontal thin long parallel wires, separated by a distance r carry current I each in the opposite directions. The net magnetic field at a point midway between them will be ______.
