Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why does current in a steady state not flow in a capacitor connected across a battery? However momentary current does flow during charging or discharging of the capacitor. Explain.
उत्तर
In steady state condition, voltage across the capacitor nearly equals to the voltage of the charging source. Hence net voltage acting in the circuit is zero. Due to this there is no flow of charge (current) through the circuit and hence the capacitor.
Now we know for an uncharged capacitor the potential difference across the capacitor is zero. So when it is connected to a battery, the battery begins to charge it by withdrawing the free electrons from one plate connected with the positive terminal of the battery of the capacitance and deposit on the other plate of the capacitor. So, due to this flow of charge, there exist a momentary current while charging of the capacitor. Now when the capacitor is fully charged i.e. voltage across the capacitor nearly equals to the voltage of the charging source, the current in the circuit vanishes.
Now in case of discharging of a charged capacitor, the battery gets replaced by a wire of say resistance R. Hence the capacitor itself acts as a battery now and flow of charge exists in the circuit from negative plate to the positive plate of the battery. This leads to momentary current in the circuit. As soon as the all the positive charges on one plate gets neutralised by the negative charges on the other plate, the flow of charge stops and hence the current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Find the value of the phase difference between the current and the voltage in the series LCR circuit shown below. Which one leads in phase : current or voltage ?
(ii) Without making any other change, find the value of the additional capacitor C1, to be connected in parallel with the capacitor C, in order to make the power factor of the circuit unity.
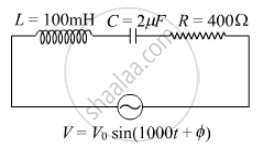
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the condition under which watt-less current flows in the circuit ?
(i) An a.c. source of emf ε = 200 sin omegat is connected to a resistor of 50 Ω . calculate :
(1) Average current (`"I"_("avg")`)
(2) Root mean square (rms) value of emf
(ii) State any two characteristics of resonance in an LCR series circuit.
Choose the correct answer from given options
The selectivity of a series LCR a.c. circuit is large, when
For a series LCR-circuit, the power loss at resonance is ______.
In a series LCR circuit the voltage across an inductor, capacitor and resistor are 20 V, 20 V and 40 V respectively. The phase difference between the applied voltage and the current in the circuit is ______.
In series LCR AC-circuit, the phase angle between current and voltage is
A series LCR circuit containing 5.0 H inductor, 80 µF capacitor and 40 Ω resistor is connected to 230 V variable frequency ac source. The angular frequencies of the source at which power transferred to the circuit is half the power at the resonant angular frequency are likely to be ______.
If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is ______.
A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source. Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the impedance of the circuit.
