Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
उत्तर
Area of the small flat search coil, A = 2 cm2 = 2 × 10−4 m2
Number of turns on the coil, N = 25
Total charge flowing in the coil, Q = 7.5 mC = 7.5 × 10−3 C
Total resistance of the coil and galvanometer, R = 0.50 Ω
Induced current in the coil,
I = `("Induced emf (e)")/"R"` ...............(1)
Induced emf is given as:
e = `-"N"("d"phi)/("dt")` ..............(2)
Where,
`"d"phi` = Charge in flux
Combining equations (1) and (2), we get
I = `-("N"("d"phi)/("dt"))/("R")`
Idt = `-"N"/"R" "d"phi` ...........(3)
Initial flux through the coil, `phi_"i"` = BA
Where,
B = Magnetic field strength
Final flux through the coil, `phi_"f"` = 0
Integrating equation (3) on both sides, we have
`int"Idt" = -"N"/"R"int_(phi_"i")^(phi_"f")"d"phi`
But total Charge Q = `int"Idt"`
∴ Q = `-"N"/"R"(phi_"f" - phi_"i") = -"N"/"R"(-phi_"i") = +("N"phi_"i")/"R"`
Q = `("NBA")/"R"`
∴ B = `("QR")/("NA")`
= `(7.5 xx 10^-3 xx 0.5)/(25 xx 2 xx 10^-4)`
= 0.75 T
Hence, the field strength of the magnet is 0.75 T.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a bar magnet is pushed towards (or away) from the coil connected to a galvanometer, the pointer in the galvanometer deflects. Identify the phenomenon causing this deflection and write the factors on which the amount and direction of the deflection depends. State the laws describing this phenomenon.
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
What do you understand by the term "electromagnetic induction"? Explain with the help of a diagram.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
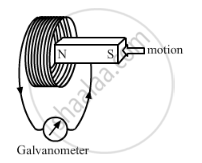
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic field. A potential difference appears across the two ends _____________ .
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
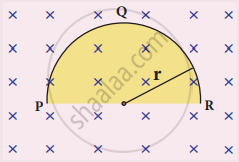
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
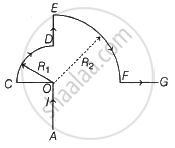
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)