Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic field. A potential difference appears across the two ends _____________ .
विकल्प
if `vec v " || "vec l`
if `vec v " || "vec B`
if `vec l " || "vec B`
None of these
उत्तर
None of these
The potential difference across the two ends is given by
`e=Bvl`
It is non-zero only
(i) if the rod is moving in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field `(vec v bot vec B)`
(ii) if the velocity of the rod is in the direction perpendicular to the length of the rod `(vec v bot vec l)`
(iii) if the magnetic field is perpendicular to the length of the rod `vec l bot vec B`
Thus, none of the above conditions is satisfied in the alternatives given.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
The most suitable material for making the core of an electromagnet is:
(a) soft iron
(b) brass
(c) aluminium
(d) steel
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
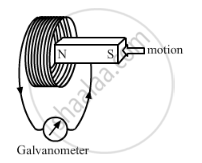
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
L, C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively. Which of the following combinations have dimensions of frequency?
(a) `1/(RC)`
(b) `R/L`
(c) `1/sqrt(LC)`
(d) C/L
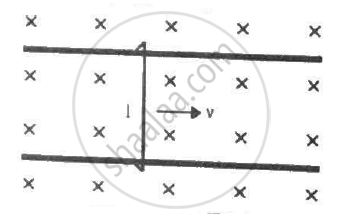
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
The diagram shows a rectangular coil ABCD, suspended freely between the concave pole pieces of a permanent horseshoe magnet, such that the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field.

(i) State your observation, when current is switched on.
(ii) Give an explanation for your observation in (i).
(iii) State the rule, which will help you to find the motion of rotation of coil.
(iv) In which position will the coil ultimately come to rest?
(v) State four ways of increasing the magnitude of force acting on the coil.
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Right hand thumb rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
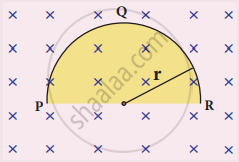
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
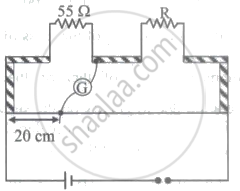
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
The primary of a transformer has 400 turns while the secondary has 2000 turns. If the power output from the secondary at 1000 Vis 12 kW, what is the primary voltage?
