Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
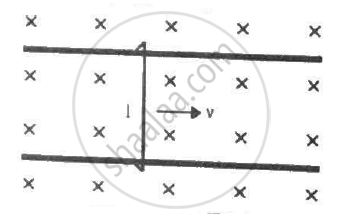
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
उत्तर
Because the force exerted by the magnetic field on the rod is given by Fmagnetic = ilB, the direction of this force is opposite to that of the motion of the rod.
Now, let the external force on it be F.
Because the velocity is constant, the net force acting on the wire must be zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
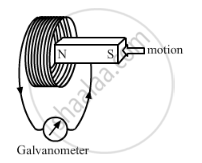
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
Name and state the law which determines the direction of induced current.
or
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
A conducting square loop having edges of length 2.0 cm is rotated through 180° about a diagonal in 0.20 s. A magnetic field B exists in the region which is perpendicular to the loop in its initial position. If the average induced emf during the rotation is 20 mV, find the magnitude of the magnetic field.
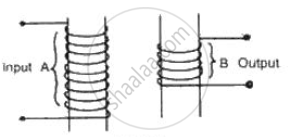
Complete the following diagram of a transformer and name the parts labeled A and B. Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram . What is the material of this part? In this transformer a step-up or step-down? Why?
Answer the following:
State the principles of the electric motor and electric generator.
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
A generator has an e.m.f. of 440 Volt and internal resistance of 4000 hm. Its terminals are connected to a load of 4000 ohm. The voltage across the load is ______.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
