Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram shows a rectangular coil ABCD, suspended freely between the concave pole pieces of a permanent horseshoe magnet, such that the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field.

(i) State your observation, when current is switched on.
(ii) Give an explanation for your observation in (i).
(iii) State the rule, which will help you to find the motion of rotation of coil.
(iv) In which position will the coil ultimately come to rest?
(v) State four ways of increasing the magnitude of force acting on the coil.
उत्तर
(i) The coil ABCD will turn. The arm AB of the coil will move out of the plane of paper and arm CD into the plane of paper. Thus, coil will turn in anticlockwise direction.
(ii) A magnetic field is set up by the coil due to the passage of electric current. The magnetic field of the coil is at right angles to the magnetic field of permanent magnet. Thus, a magnetic couple acts, which turns the coil.
(iii) Fleming’s left rule: It states: Stretch the thumb, the forefinger and the middle finger of left hand, such that forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field; middle finger points in the direction of current. Then, the thumb points in the direction of motion of conductor.
(iv) The coil will come to rest at right angles to the direction of magnetic field.
(v)
(a) By increasing the number of turns in coil.
(b) By increasing the area of cross-section of coil.
(c) By placing laminated soft iron core within the coil.
(d) By increasing the magnitude of the current coil.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
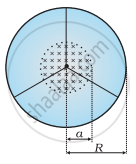
A line charge λ per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim of a wheel of mass M and radius R. The wheel has light non-conducting spokes and is free to rotate without friction about its axis (Figure). A uniform magnetic field extends over a circular region within the rim. It is given by,
B = − B0 k (r ≤ a; a < R)
= 0 (otherwise)
What is the angular velocity of the wheel after the field is suddenly switched off?
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
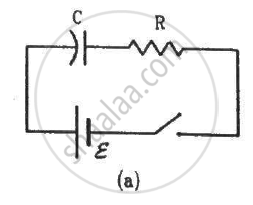
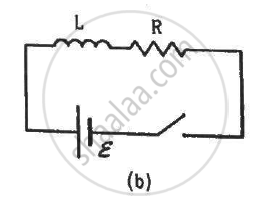
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
