Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
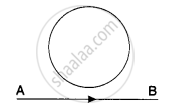
A conducting loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field with its plane perpendicular to the field. An emf is induced in the loop if ___________.
विकल्प
- it is translated.
- it is rotated about its axis.
- both it is translated and it is rotated about its axis.
- it is rotated about its diameter.
उत्तर
A conducting loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field with its plane perpendicular to the field. An emf is induced in the loop if it is rotated about its diameter.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Figure shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutual perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod = 15 cm, B = 0.50 T, resistance of the closed loop containing the rod = 9.0 mΩ. Assume the field to be uniform.
(a) Suppose K is open and the rod is moved with a speed of 12 cm s−1 in the direction shown. Give the polarity and magnitude of the induced emf.
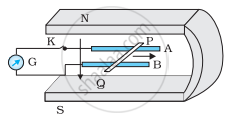
(b) Is there an excess charge built up at the ends of the rods when K is open? What if K is closed?
(c) With K open and the rod moving uniformly, there is no net force on the electrons in the rod PQ even though they do experience magnetic force due to the motion of the rod. Explain.
(d) What is the retarding force on the rod when K is closed?
(e) How much power is required (by an external agent) to keep the rod moving at the same speed = (12 cm s−1) when K is closed? How much power is required when K is open?
(f) How much power is dissipated as heat in the closed circuit? What is the source of this power?
(g) What is the induced emf in the moving rod if the magnetic field is parallel to the rails instead of being perpendicular?
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
A metallic rod of ‘L’ length is rotated with angular frequency of ‘ω’ with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius L, about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is presents everywhere. Deduce the expression for the emf between the centre and the metallic ring.
A conducting circular loop having a radius of 5.0 cm, is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.50 T. It is removed from the field in 0.50 s. Find the average emf produced in the loop during this time.
A conducting loop of area 5.0 cm2 is placed in a magnetic field which varies sinusoidally with time as B = B0 sin ωt where B0 = 0.20 T and ω = 300 s−1. The normal to the coil makes an angle of 60° with the field. Find (a) the maximum emf induced in the coil, (b) the emf induced at τ = (π/900)s and (c) the emf induced at t = (π/600) s.
A wire-loop confined in a plane is rotated in its own plane with some angular velocity. A uniform magnetic field exists in the region. Find the emf induced in the loop.
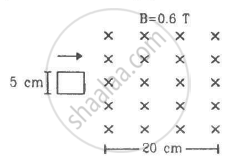
Figure shows a square loop of side 5 cm being moved towards right at a constant speed of 1 cm/s. The front edge enters the 20 cm wide magnetic field at t = 0. Find the emf induced in the loop at (a) t = 2 s, (b) t = 10 s, (c) t = 22 s and (d) t = 30 s.
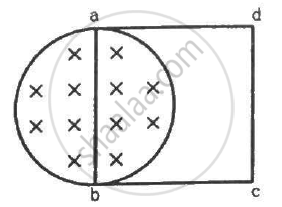
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10 cm as shown in figure. A uniform wire of length 80 cm and resistance 4.0 Ω is bent into a square frame and is placed with one side along a diameter of the cylindrical region. If the magnetic field increases at a constant rate of 0.010 T/s, find the current induced in the frame.
A metallic metre stick moves with a velocity of 2 m s−1 in a direction perpendicular to its length and perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.2 T. Find the emf induced between the ends of the stick.
A wire of length 10 cm translates in a direction making an angle of 60° with its length. The plane of motion is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 1.0 T that exists in the space. Find the emf induced between the ends of the rod if the speed of translation is 20 cm s−1.
Consider a situation similar to that of the previous problem except that the ends of the rod slide on a pair of thick metallic rails laid parallel to the wire. At one end the rails are connected by resistor of resistance R. (a) What force is needed to keep the rod sliding at a constant speed v? (b) In this situation what is the current in the resistance R? (c) Find the rate of heat developed in the resistor. (d) Find the power delivered by the external agent exerting the force on the rod.
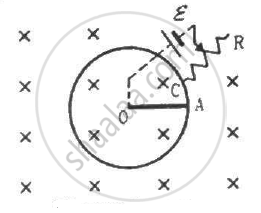
Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. A battery of emf ε and a variable resistance R are connected between O and C. Neglect the resistance of the connecting wires. Let θ be the angle made by the rod from the horizontal position (show in the figure), measured in the clockwise direction. During the part of the motion 0 < θ < π/4 the only forces acting on the rod are gravity and the forces exerted by the magnetic field and the pivot. However, during the part of the motion, the resistance R is varied in such a way that the rod continues to rotate with a constant angular velocity ω. Find the value of R in terms of the given quantities.
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region, shown dotted in figure. The magnetic field increases at a constant rate `(dB)/(dt).` Consider a circle of radius r coaxial with the cylindrical region. (a) Find the magnitude of the electric field E at a point on the circumference of the circle. (b) Consider a point P on the side of the square circumscribing the circle. Show that the component of the induced electric field at P along ba is the same as the magnitude found in part (a).

The mutual inductance between two coils is 2.5 H. If the current in one coil is changed at the rate of 1 As−1, what will be the emf induced in the other coil?
An alternating emf of 110 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistance R of 80 Ω and an inductor L in series. The current is found to lag behind the supply voltage by an angle 8 = tan-1 (3/4). Find the :
(i) Inductive reactance
(ii) Impedance of the circuit
(iii) Current flowing in the circuit
(iv) If the inductor has a coefficient of self-inductance of 0.1 H, what is the frequency of the applied emf?
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance ______.
In the given figure current from A to B in the straight wire is decreasing. The direction of induced current in the loop is A ______.