Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following:
State the principles of the electric motor and electric generator.
Solution
- Principle of electric motor:
Electric motor works on the principle that a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force. - Principle of electric generator:
Electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When the coil of electric generator rotates in a magnetic field. The magnetic field induces a current in this coil. This induced current then flows into circuit connected to the coil.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
What is electromagnetic induction?
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using:
(a) Fleming's right-hand rule
(b) Fleming's left-hand rule
(c) Clock face rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
A conducting square loop having edges of length 2.0 cm is rotated through 180° about a diagonal in 0.20 s. A magnetic field B exists in the region which is perpendicular to the loop in its initial position. If the average induced emf during the rotation is 20 mV, find the magnitude of the magnetic field.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-up transformer.
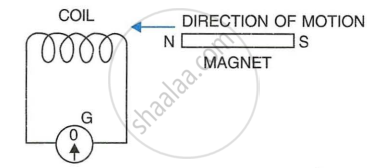
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
Why soft iron is preferred to be used as the core of the electromagnet of an electric bell?
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
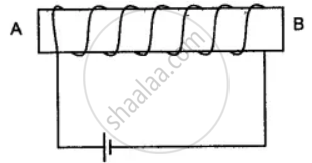
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : _______
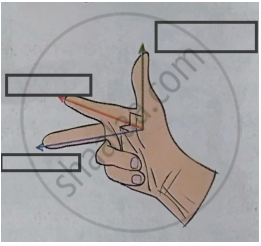
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
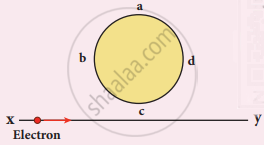
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
Name some equipment that uses electromagnetism for functioning.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
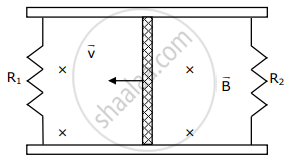
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
