Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What determines the frequency of a.c. produced in a generator?
Solution
The number of coil rotations, or alternating e.m.f., determines the frequency of the a.c. produced in the generator. Induced e.m.f. (e = e0 sin 2π nt) where n is the number of rotation made by coil per second and the current i = i0 sin 2π nt.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the principle of an electric generator.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is pushed into the coil?
What change should be made in an a.c. generator so that it may become a d.c. generator?
What is the function of brushes in an electric generator?
Complete the following sentence:
A generator with commutator produces ............... current.
Each one of the following changes will increase emf (or voltage) in a simple generator except:
(a) increasing the number of turns in the armature coil
(b) winding the coil on a soft iron armature
(c) increasing the size of the gap in which the armature turns
(d) increasing the speed of rotation
Explain the difference:
AC generator and DC generator.
The given figures 1 to 3 show the working of a simple A.C. generator. Study the diagrams and answers of the following questions.
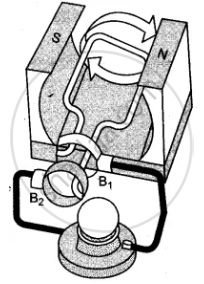
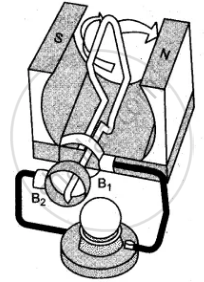
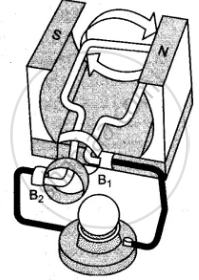
(i) State and explain the principle underlying the working of a simple generator.
(ii) Where is the loop of wire placed?
(iii) What happens when the loop is rotated?
(iv) Indicate the direction of the current flow through the wire for the first half of the turn (in first figure). Name and state the rule used in finding the direction of the current.
(v) Indicate the direction of the current for the case shown in second figure.
(vi) Indicate the direction of current in the outer circuit (i.e., electric bulb) in first and third figure.
(vii) What type of current is shown in the above diagrams? Explain.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer forming a loop and a magnet is:
A: Held stationary
B: Moved away along its axis
C: Moved towards along its axis
D: There will be an induced current in
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil?
