Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : _______
उत्तर
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : Number of convex lenses two
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
To determine the approximate focal length of the given convex lens by focussing a distant object (say, a sign board), you try to focus the image of the object on a screen. The image you obtain on the screen is always
(a) erect and laterally inverted
(b) erect and diminished
(c) inverted and diminished
(d) virtual, inverted and diminished
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
"A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
A student has obtained a magnified image of a flame on a screen using a convex lens. To draw the corresponding ray diagram to show the image formation, which of the following two rays whose paths after refraction are shown, should he select ?
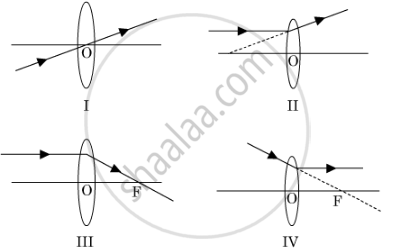
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and III
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
An object AB is placed between O and F1 on the principal axis of a converging lens as shown in the diagram.
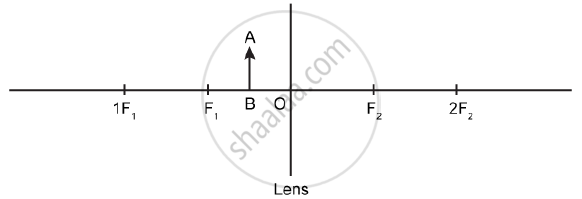
Copy the diagram and by using three standard rays starting from point A, obtain an image of the object AB.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its real, inverted and magnified image?
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Explain with the help of a diagram, why the convex lens is also called a converging lens.
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
A burning candle whose flame is 1.5 cm tall is placed at a certain distance in front of a convex lens. An image of candle flame is received on a white screen kept behind the lens. The image of flame also measures 1.5 cm. If f is the focal length of convex lens, the candle is placed:
(a) at f
(b) between f and 2f
(c) at 2f
(d) beyond 2f
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
A beam of parallel light rays is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the diagram below:
Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) a rectangular glass block
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a glass prism
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted magnified image?
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted diminished image?
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

The focal length of a thin convex lens is ______ than that of a thick convex lens.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens. State three characteristics of the image.
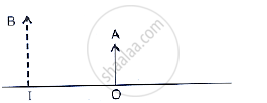
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is
(A)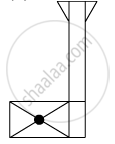
(B)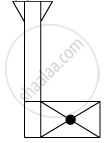
(C)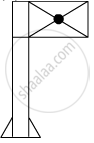
(D)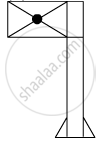
Observe the following figure and complete the table:

| Points | Answer |
| (i) Position of the object | |
| (ii) Position of the image | |
| (iii) Size of the image | |
| (iv) Nature of the image |
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
A concave mirror and convex lens are held in water. What changes, if any, do you expect in their focal length?
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
