Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
उत्तर
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : Image at infinity
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of height 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical 'O', principal focus F and height of the image on the diagram.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
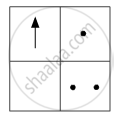
(a)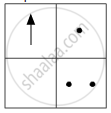
(b)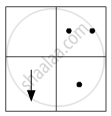
(c)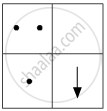
(d)
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –100 | +25 |
| 2 | –60 | +30 |
| 3 | –40 | +40 |
| 4 | –30 | +60 |
| 5 | –25 | +100 |
| 6 | –15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification.
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
A ray of light travelling in water emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
A 1 cm high object is placed at a distance of 2f from a convex lens. What is the height of the image formed?
If an object is at a considerable distance (or infinity) in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
A convex lens of focal length 0.10 m is used to form a magnified image of an object of height 5 mm placed at a distance of 0.08 m from the lens. Calculate the position, nature and size of the image.
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.50 m
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
In a certain murder investigation, it was important to discover whether the victim was long-sighted or short-sighted. How could a detective decide by examining his spectacles?
Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a convex lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms.
Study the diagram below.
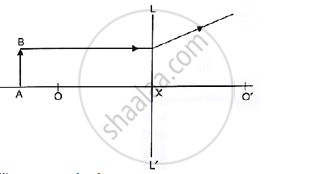
what are the points O, O’ called?
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
The focal length of a lens is positive. In this case, state the kind of lens.
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in observing biological specimens.
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
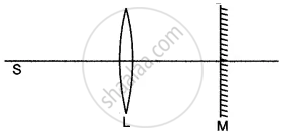
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
An object is placed in front of a convex lens such that the image formed has the same size as that of the object. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this.
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
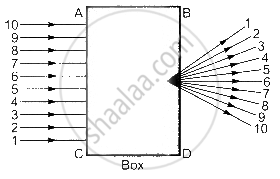
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as show in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
- In which type of microscope do you find the lens arrangement as shown in the following diagram?

- Write about the working and the use of this microscope.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
