Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
उत्तर
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : Image at infinity
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
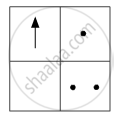
(a)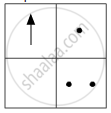
(b)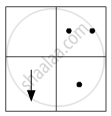
(c)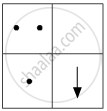
(d)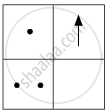
When a ray of light enters from one medium to another having different optical densities it bends. Why does this phenomenon occur?
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
Complete the following table:
| Instrument | Number of Convex Lenses |
Use |
| Simple Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Compound Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Telescope | .............. | .............. |
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
For what position of an object a real, diminished image is formed by a convex lens?
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
A convex lens of focal length 0.10 m is used to form a magnified image of an object of height 5 mm placed at a distance of 0.08 m from the lens. Calculate the position, nature and size of the image.
A camera fitted with a lens of focal length 50 mm is being used to photograph a flower that is 5 cm in diameter. The flower is placed 20 cm in front of the camera lens.
At what distance from the film should the lens be adjusted to obtain a sharp image of the flower?
Complete the following sentence.
A long-sighted person cannot see ........... objects clearly. Long-sightedness can be corrected by using .............. lenses.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.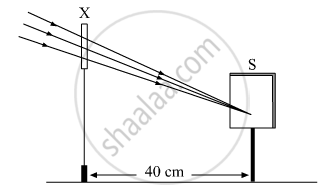
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: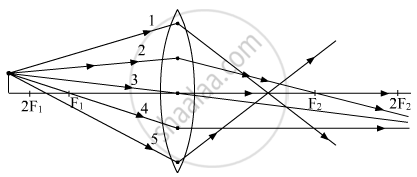
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
State two applications of a convex lens.
How will you decide whether a given piece of glass is a concave lens, convex lens, or a plane glass plate?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
Define the principal focus of a convex lens.
Define the terms principal foci and focal lengths as applied to a convex lens, and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
Convex lens is also known as ______.
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
 |
 |
The above images are that of a specialized slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray.
To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
a. Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, what kind of lens must the slide projector have?
b. If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance then with one reason state what will be the sign for `"𝑣"/"𝑢"` in the given case?
c. A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector’s lens so that the slide is in focus?
OR
c. When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation. (not to scale)
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
