Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Nearsightedness: elongated eyeball : : farsightedness: _______
उत्तर
Nearsightedness: elongated eyeball : : farsightedness: flattening of eye ball
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given below is a diagram showing a defect of human eye. Study it and answer the following questions.
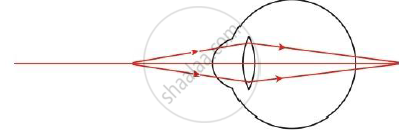
(i) Name the defect shown in the figure.
(ii) Give reason for this defect of eye in human being.
(iii) Name the type of lens used to correct the eye defect.
Do you know that the corneal-impairment can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of the donated eye? How and why should we organise groups to motivate the community members to donate their eyes after death?
List three common refractive defects of vision. Suggest the way of correcting these defects.
What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Name the defect of vision in a person:
whose near point is more than 25 on away.
Name the body part with which the terms myopia and hypermetropia are connected.
A student sitting in the last row of the class-room is not able to read clearly the writing on the blackboard.
How can this defect by corrected?
Explain with the help of labelled ray-diagram, the defect of vision called hypermetropia, and hot it is corrected by a lens.
A person suffering from the eye-defect myopia (short-sightedness) can see clearly only up to a distance of 2 metres. What is the nature and power of lens required to rectify this defect?
The near-point of a person suffering from hypermetropia is at 50 cm from his eye. What is the nature and power of the lens needed to correct this defect? (Assume that the near-point of the normal eye is 25 cm).
An eye has a far point of 2 m. What type of lens in spectacles would be needed to increase the far point to infinity? Also calculate the power of lens required. Is this eye long-sighted or short-sighted?
The defect of vision in which the eye-lens of a person gets progressively cloudy resulting in blurred vision is called:
(a) myopia
(b) presbyopia
(c) colourblindness
(d) cataract
To read a book held at a distance of 25 cm, will she need converging or diverging spectacle lenses?
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Rods and cones (sensitivity).
Name an old age eye defect. What happens in it?
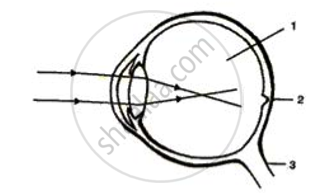
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the question that follow:
Name the defect shown in the diagram.
A person is unable to see distinctly the objects closer than 1 m. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw ray diagrams to illustrate the cause of the defect and its correction by suitable lens.
A person cannot read newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eyes. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this defect. List its two possible causes. Draw a ray diagram to show how this defect may be corrected using a lens of appropriate focal length.
A student cannot see a chart hanging on a wall placed at a distance of 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. How can it be corrected? Draw ray diagrams for the (i) defect of vision and also (ii) for its correction.
List two causes of presbyopia. Draw labelled diagram of a lens used for the correction of this defect of vision.
When do we consider a student sitting in the class to be myopic? List two causes of this defect. Explain using a ray diagram how this defect of eye can be corrected.
Select the odd one in the following series:
Endolymph, Tympanic membrane, Semi-circular canal, Blind spot.
Write whether the following is true or false:
A convex lens is used for correcting myopia.
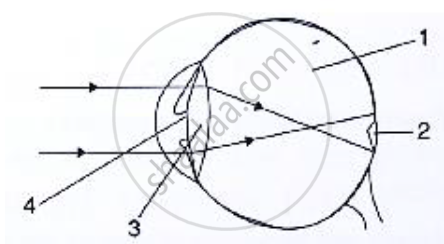
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
(iii) Give labelled two possible reasons for this eye defect.
(iv) Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified.
The near point of the eye of a person is 50 cm. Find the nature and power of the corrective lens required by the person to enable him to see clearly the objects placed at 25 cm from the eye?
Give Reason:
When you enter into a dark room from bright because of sunlight, you can not see things for a few seconds.
What type of lens is used to correct Astigmatism?
What type of lens is used to correct Hypermetropia?
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
Hypermetropia is a defect of the eye caused due to the eyeball elongation
Assertion: Myopia is the defect of vision in which a person cannot see distant objects clearly.
Reason: This due to eye-ball being too short.
Myopia may arise due to ____________.
Which of the following statement is correct?
Draw ray diagram showing myopic eye.
A person needs a lens of power –4.5 D for correction of her vision.
- What kind of defect in vision is she suffering from?
- What is the focal length of the corrective lens?
- What is the nature of the corrective lens?
State reasons for Myopia. With the help of ray diagrams, show the:
- image formation by a myopic eye, and
- correction of myopia using an appropriate lens.
Observe the following diagram and answer questions following it:

- Identify the defect of vision shown.
- List its two causes.
- Name the type of lens used for the correction of this defect.
Complete the following table by observing the given figures:
| Figure → | 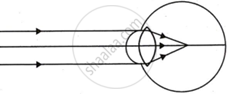 |
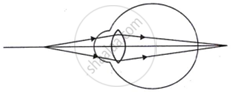 |
| Points ↓ | ||
| (a) Name of the defect | ______ | ______ |
| (b) Position of the image | ______ | ______ |
| (c) Lens used to correct the defect | ______ | ______ |
