Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Nearsightedness: elongated eyeball : : farsightedness: _______
Solution
Nearsightedness: elongated eyeball : : farsightedness: flattening of eye ball
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
List three common refractive defects of vision. Suggest the way of correcting these defects.
the biological/technical terms for the lens of eye losing flexibility resulting in a kind of long-sightedness in middle aged people.
A student is unable to see clearly the words written on the black board placed at a distance of approximately 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. State the possible causes of this defect and explain the method of correcting it.
What is the other name for
myopia
What is the other name for
hypermetropia
What is the scientific name of
long-sightedness?
Name the defect of vision in which the eye-lens loses its power of accommodation due to old age.
Name the defect of vision which makes the eye-lens cloudy resulting in blurred vision.
A student sitting in the last row of the class-room is not able to read clearly the writing on the blackboard.
How can this defect by corrected?
Differentiate between myopia and hypermetropia. What type of spectacles should be worn by a person having the defects of myopia as well as hypermetropia? How does it help?
The near-point of a person suffering from hypermetropia is at 50 cm from his eye. What is the nature and power of the lens needed to correct this defect? (Assume that the near-point of the normal eye is 25 cm).
What is long-sightedness? State the two causes of long-sightedness (or hypermetropia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect long-sightedness.
(ii) correction of long-sightedness by using a lens.
An eye has a near point distance of 0.75 m. What sort of lens in spectacles would be needed to reduce the near point distance to 0.25 m? Also calculate the power of lens required. Is this eye long-sighted or short-sighted?
Though a woman can see the distant object clearly, she cannot see the nearby objects clearly. She is suffering from the defect of vision called:
(a) long-sight
(b) short-sight
(c) hind-sight
(d) mid-sight
The defect of vision in which the eye-lens of a person gets progressively cloudy resulting in blurred vision is called:
(a) myopia
(b) presbyopia
(c) colourblindness
(d) cataract
A short-sighted person has a near point of 15 cm and a far point of 40 cm.
(a) Can he see clearly an object at a distance of:
(i) 5 cm?
(ii) 25 cm?
(iii) 50 cm?
(b) To see clearly an object at infinity, what kind of spectacle lenses does he need?
A person can read a book clearly only if he holds it at an arm's length from him. Name the defect of vision:
if the person is a young man
Which part of the eye is grafted in a needy patient from a donated eye?
Name the following:
The photosensitive pigment present in the rods of the retina.
What is meant by optical illusion? Give one example.
State one role of ciliary muscles in the human eye.
An old man cannot see objects closer than 1 m from the eye clearly. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. How can it be corrected? Draw ray diagram for the (i) defect of vision and also (ii) for its correction.
List two causes of presbyopia. Draw labelled diagram of a lens used for the correction of this defect of vision.
The near point of the eye of a person is 50 cm. Find the nature and power of the corrective lens required by the person to enable him to see clearly the objects placed at 25 cm from the eye?
A person is unable to see objects distinctly placed within 50 cm from his eyes.
(a) Name the defect of vision the person is suffering from and list its two possible causes.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the defect in the above case.
(c) Mention the type of lens used by him for the correction of the defect and calculate its power. Assume that the near point for the normal eye is 25 cm.
(d) Draw a labeled diagram for the correction of the defect in the above case.
Name an old age eye defect. Why is it caused?
Give Reason:
Why do we see clearly in the central region of the retina?
Give Reason:
Deficiency of vitamin A causes night blindness.
Explain the Term: Cataract
The diagram given below represents the cross-section of the human eye:

(i) Name the parts labeled 1—12.
(ii) What is the function of the part marked ‘10’?
(iii) What would happen if part ‘5’ is damaged or cut?
Nearsightedness : concave lens : : farsightedness : _______
Write scientific reason.
Nearsightedness, this defect can be corrected by using spectacles with concave lens.
Observe the given below the figure, correct it and explain and write about the concept depicted in this figure.
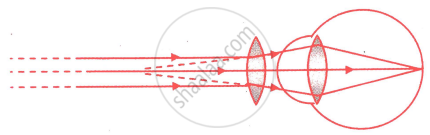
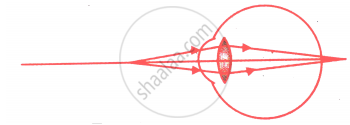
Given below is a diagram showing a defect of vision. Name the defect of vision and draw an accurately labelled diagram to correct this defect.
A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power:
Which of the following statement is correct?
Draw ray diagram showing myopic eye.
A person is unable to see clearly a poster fixed on a distant wall. He however sees it clearly when standing at a distance of about 2 m from the wall.
- Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by his eye lens when he is far away from the wall.
- List two possible reasons of this defect of vision.
- Draw ray diagram to show the correction of this defect using appropriate lens.
