Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A short-sighted person has a near point of 15 cm and a far point of 40 cm.
(a) Can he see clearly an object at a distance of:
(i) 5 cm?
(ii) 25 cm?
(iii) 50 cm?
(b) To see clearly an object at infinity, what kind of spectacle lenses does he need?
Solution
a) (i) A short-sighted person with a near point of 15 cm and a far point of 40 cm in front of the eye cannot clearly see an object at a distance of 5 cm because he can see an object only when it is placed at his near point (i.e., 15 cm).
(b) A short-sighted person can clearly see an object at a distance of 25 cm as it the normal near point of the eye. Moreover, the person's far point is located at 40 cm from the eye.
(c) The person cannot see the object clearly as it is at a distance of 50 cm, which is beyond his far point.
(d) In order to see an object clearly at infinity, the person should use concave lenses in his spectacles. A concave lens first diverges the light rays from the object at infinity to form a virtual image at the eye's far point. The eye lens then easily focusses the rays from the eye's far point to form a clear image on the retina.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the following:
The photosensitive pigment present in the rods of the retina.
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in bracket.
Myopia and hyperopia (cause of the defect)
Observer the following diagram and answer the questions.
a) Which eye defect is shown in this diagram?
b) What are the possible reasons for this eye defect?
c) How this defect is corrected, write it in brief?
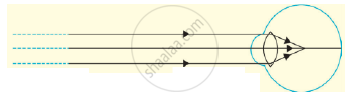
When do we consider a student sitting in the class to be myopic? List two causes of this defect. Explain using a ray diagram how this defect of eye can be corrected.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the question that follow:
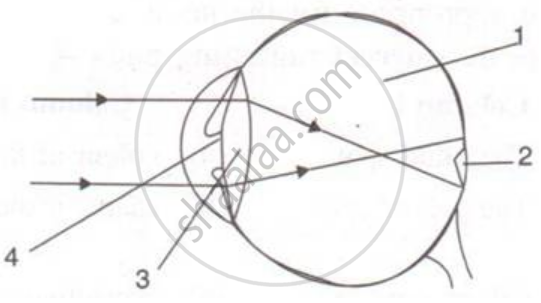
Name the parts labeled 1 to 4.
Give Reason:
Deficiency of vitamin A causes night blindness.
Given below is a diagrammatic representation of a defect of the human eye:
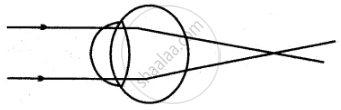
(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Mention two reasons for the above defect.
(iii) State how the defect can be rectified.
(iv) Name the part of the eye responsible for maintaining the shape of the eyeball.
Choose the Odd One Out:
Nearsightedness: elongated eyeball : : farsightedness: _______
Correlate the given sequence:
Hypermetropia : Convex lens : ______ : Concave lens
