Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
पर्याय
power 2 D; convex lens
power 1 D; concave lens
power - 0.5 D; concave lens
power - 0.25 D; convex lens
उत्तर
power 2 D; convex lens
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
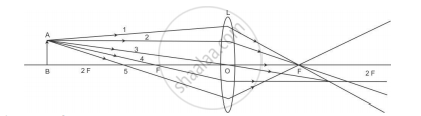
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Define principal axis, principal focus and focal length of a convex lens.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
You eye contains a convex lens. Why is it unwise to look at the sun?
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
How would a pencil look like if you saw it through How would a pencil look like if you saw it through
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

Study the diagram below.
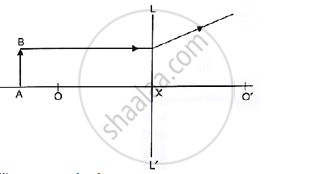
what are the points O, O’ called?
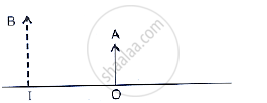
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens. State three characteristics of the image.
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
To find the image distance for varying object distances in case of a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object by placing it at 20 cm distance from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object away from the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-towards or away from the lens does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) How does the size of image change?
(c) Approximately at what distance does he obtain the image of magnification –1?
(d) How does the intensity of image change as the object moves farther and farther away from the lens?
List four properties of the image formed by a convex mirror.
A lens always forms an image between the object and the lens.
A lens always forms an image between the object and the lens.
State two applications of a convex lens.
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in cine projector.
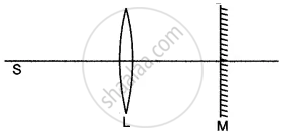
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.
- In which type of microscope do you find the lens arrangement as shown in the following diagram?

- Write about the working and the use of this microscope.
 |
 |
The above images are that of a specialized slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray.
To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
a. Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, what kind of lens must the slide projector have?
b. If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance then with one reason state what will be the sign for `"𝑣"/"𝑢"` in the given case?
c. A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector’s lens so that the slide is in focus?
OR
c. When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation. (not to scale)
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
