Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
विकल्प
power 2 D; convex lens
power 1 D; concave lens
power - 0.5 D; concave lens
power - 0.25 D; convex lens
उत्तर
power 2 D; convex lens
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
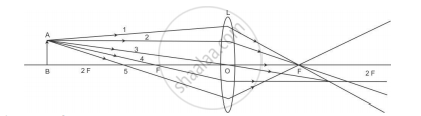
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
A student has obtained a magnified image of a flame on a screen using a convex lens. To draw the corresponding ray diagram to show the image formation, which of the following two rays whose paths after refraction are shown, should he select ?
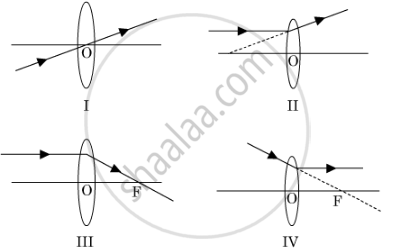
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and III
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

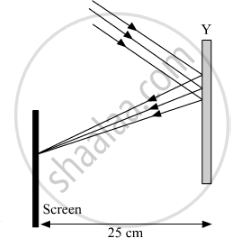
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
When a ray of light enters from one medium to another having different optical densities it bends. Why does this phenomenon occur?
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
State whether convex lens has a real focus or a virtual focus.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.50 m
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
An image formed on a screen is three times the size of the object. The object and screen are 80 cm apart when the image is sharply focussed.
State which type of lens is used.
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

A convex lens is placed in water. Its focal length will ______.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
If you are to determine to focal length of a convex lens, you should have
(A) a convex lens and a screen
(B) a convex lens and a lens holder
(C) a lens holder, a screen holder and a scale
(D) a convex lens, a screen, holder for them and a scale
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
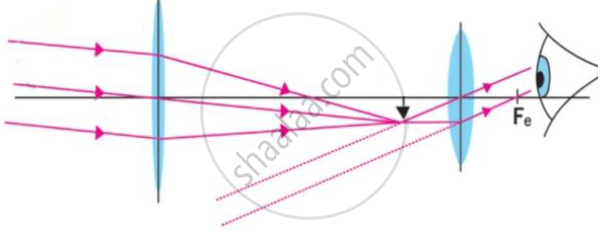
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of astronomical telescope.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

We can burn a piece of paper by focussing the sun rays by using a particular type of lens. Name the type of lens used for the above purpose. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
 |
 |
The above images are that of a specialized slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray.
To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
a. Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, what kind of lens must the slide projector have?
b. If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance then with one reason state what will be the sign for `"𝑣"/"𝑢"` in the given case?
c. A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector’s lens so that the slide is in focus?
OR
c. When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation. (not to scale)
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
