Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
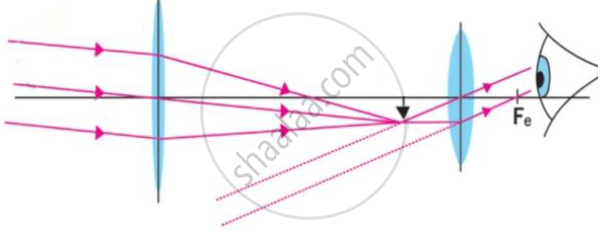
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
उत्तर
a) Arrangement of lenses shown in the figure is refracting telescope.
b) 1) object lens collect the light coming form the distant object and forms the image
2)The image works as object for the eye piece which forms the final image.
c) We can get different magnifications by using the eye piece with different focal lengths.
d)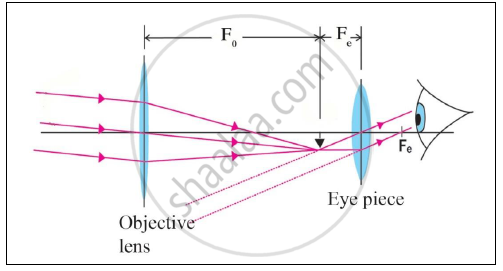
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
When a ray of light enters from one medium to another having different optical densities it bends. Why does this phenomenon occur?
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
The diagram given alongside shows a ray of light entering a rectangular block of glass.
(a) Copy the diagram and draw the normal at the point of entry.
(b) Draw the approximate path of the ray of light through the glass block and out of the other side.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass?
State any two uses of convex lenses.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are refracted by a convex lens to a point called the ........
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
What is the position of image when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm?
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
An object 50 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. Its 20 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 10 cm from the lens. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
In a certain murder investigation, it was important to discover whether the victim was long-sighted or short-sighted. How could a detective decide by examining his spectacles?
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
Where is the image formed?
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.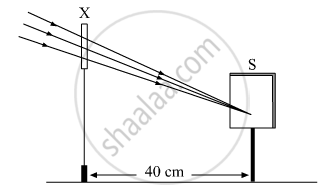
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Observe the following figure and complete the table:

| Points | Answer |
| (i) Position of the object | |
| (ii) Position of the image | |
| (iii) Size of the image | |
| (iv) Nature of the image |
(a) What type of a lens can be used as a magnifying glass?
(b) Show by a ray diagram the formation of a real image by simple magnifying lens.
Where must a point source of light be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain a parallel beam of light?
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
An object 4.0 cm in size, is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm.
(i) At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
(ii) Find the size of the image.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
A candle is placed between f and 2f a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram showing the position of the image.
Define the terms principal foci and focal lengths as applied to a convex lens, and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
