Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram given alongside shows a ray of light entering a rectangular block of glass.
(a) Copy the diagram and draw the normal at the point of entry.
(b) Draw the approximate path of the ray of light through the glass block and out of the other side.
उत्तर
(a)
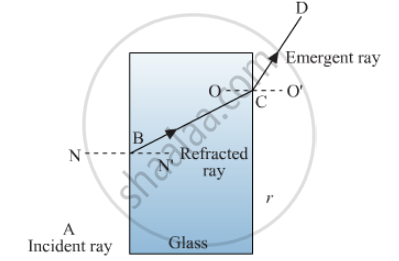
NN' is the normal at the point of entry.
(b) BC shows the path of light ray through the glass block and CD shows the path on the other side of the glass block.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
What type of lens would you use as a magnifying glass? How close must the object be to the lens?
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
Describe the nature of image formed when an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Name the lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in cine projector.
