Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram given alongside shows a ray of light entering a rectangular block of glass.
(a) Copy the diagram and draw the normal at the point of entry.
(b) Draw the approximate path of the ray of light through the glass block and out of the other side.
उत्तर
(a)
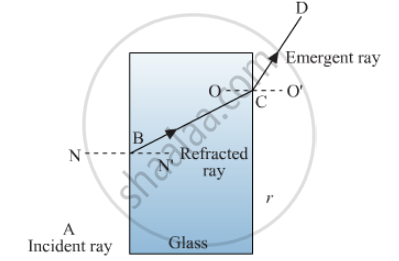
NN' is the normal at the point of entry.
(b) BC shows the path of light ray through the glass block and CD shows the path on the other side of the glass block.
संबंधित प्रश्न
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

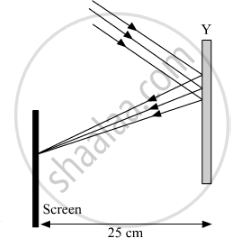
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
Observe the following figure and complete the table:

| Points | Answer |
| (i) Position of the object | |
| (ii) Position of the image | |
| (iii) Size of the image | |
| (iv) Nature of the image |
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
