Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
उत्तर
When an object is placed between the focus and the optical centre of a convex lens, a virtual and erect image of the object is formed.
When the object is placed between the focus F1 and optical centre O:
In this case, the image is formed on the same side as the object. This image is virtual, erect, and very large in size. It is formed behind 2F1.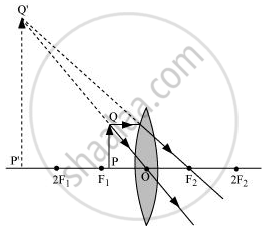
P’Q’ is the image.
PQ is the object.
F2 is the focus on the other side of the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
A student has obtained a magnified image of a flame on a screen using a convex lens. To draw the corresponding ray diagram to show the image formation, which of the following two rays whose paths after refraction are shown, should he select ?
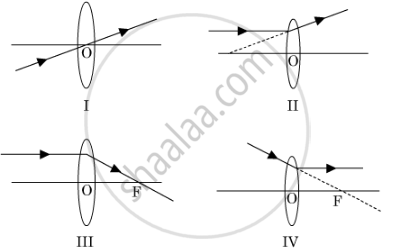
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and III
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
While determining the focal length of a convex lens, you try to focus the image of a distant object formed by the lens on the screen. The image formed on the screen, as compared to the object, should be
(A) erect and highly diminished
(B) erect and enlarged
(C) inverted and enlarged
(D) inverted and highly diminished
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
If you are to determine to focal length of a convex lens, you should have
(A) a convex lens and a screen
(B) a convex lens and a lens holder
(C) a lens holder, a screen holder and a scale
(D) a convex lens, a screen, holder for them and a scale
