Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the name.
The lens used in simple microscope.
उत्तर
The lens used in simple microscope- Convex
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –100 | +25 |
| 2 | –60 | +30 |
| 3 | –40 | +40 |
| 4 | –30 | +60 |
| 5 | –25 | +100 |
| 6 | –15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
The diagram given alongside shows a ray of light entering a rectangular block of glass.
(a) Copy the diagram and draw the normal at the point of entry.
(b) Draw the approximate path of the ray of light through the glass block and out of the other side.
f the image formed by a convex lens is of the same size as that of the object, what is the position of the image with respect to the lens?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its real, inverted and magnified image?
Define principal axis, principal focus and focal length of a convex lens.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What is the focal length of this lens?
A beam of parallel light rays is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the diagram below:
Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) a rectangular glass block
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a glass prism
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
Complete the following sentence.
A long-sighted person cannot see ........... objects clearly. Long-sightedness can be corrected by using .............. lenses.
Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a convex lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
An object 4.0 cm in size, is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm.
(i) At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
(ii) Find the size of the image.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
What is the difference between a double convex and a bi-convex lens?
How will you decide whether a given piece of glass is a concave lens, convex lens, or a plane glass plate?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
Write the three characteristics of the image formed by a convex lens of focal length 20 cm for the object at distance (i) 10 cm, (ii) 30 cm, (iii) 40 cm, (iv) 60 cm from the lens.
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
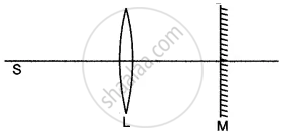
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
A candle is placed between f and 2f a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram showing the position of the image.
An object is placed in front of a convex lens such that the image formed has the same size as that of the object. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this.
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
- In which type of microscope do you find the lens arrangement as shown in the following diagram?

- Write about the working and the use of this microscope.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
